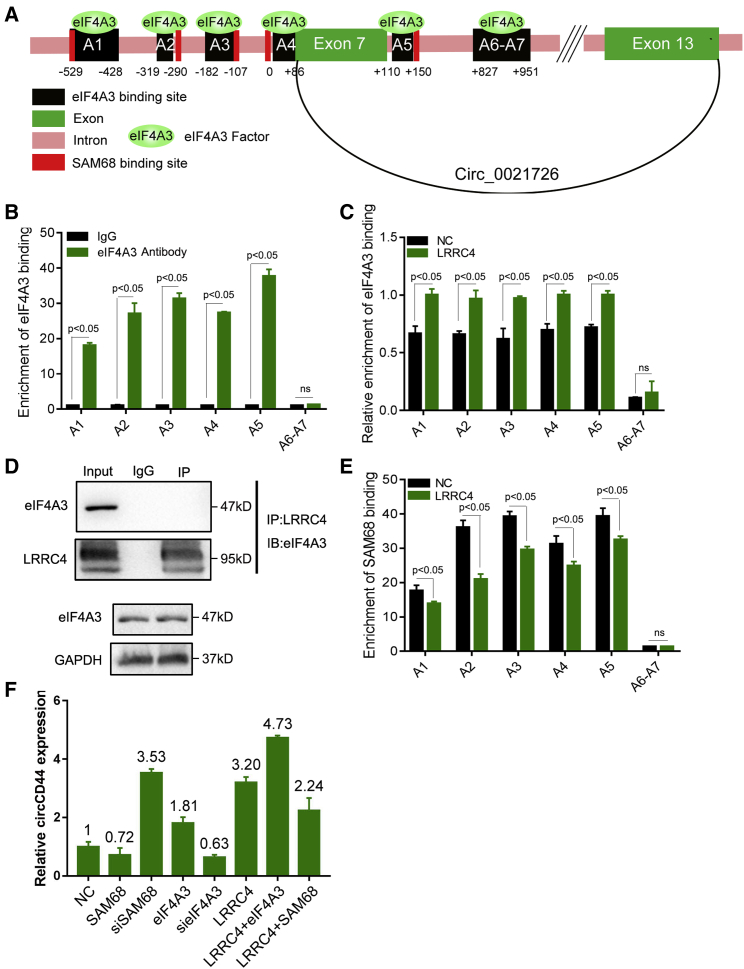
Figure 2.
LRRC4 promotes the generation of circCD44 by inhibiting the binding between SAM68 and CD44 pre-mRNA
(A) Schematic sequence diagram of hsa_circ_0021726 in CD44 pre-mRNA. Black boxes represent eIF4A3 binding sites, and red boxes represent SAM68 binding sites. (B) The RIP assay in 1124C cells showed that eIF4A3 can bind with CD44 mRNA through five putative binding sites, which we named A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5, but not A6 to A7. (C) The RIP assay in 1124C cells showed that overexpression of LRRC4 enhanced eIF4A3 binding to the five putative binding sites in CD44 pre-mRNA. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation with LRRC4 antibody showed that LRRC4 does not interact with eIF4A3 (top). Immunoblotting showed that overexpression of LRRC4 does not alter the expression of eIF4A3 (bottom). (E) The RIP assay in 1124C cells showed that overexpression of LRRC4 decreased SAM68 binding to the five putative binding sites in CD44 pre-mRNA. (F) RT-qPCR analyses showed that the expression of hsa_circ_0021726 was regulated under the respective treatment condition in 1124C cells.