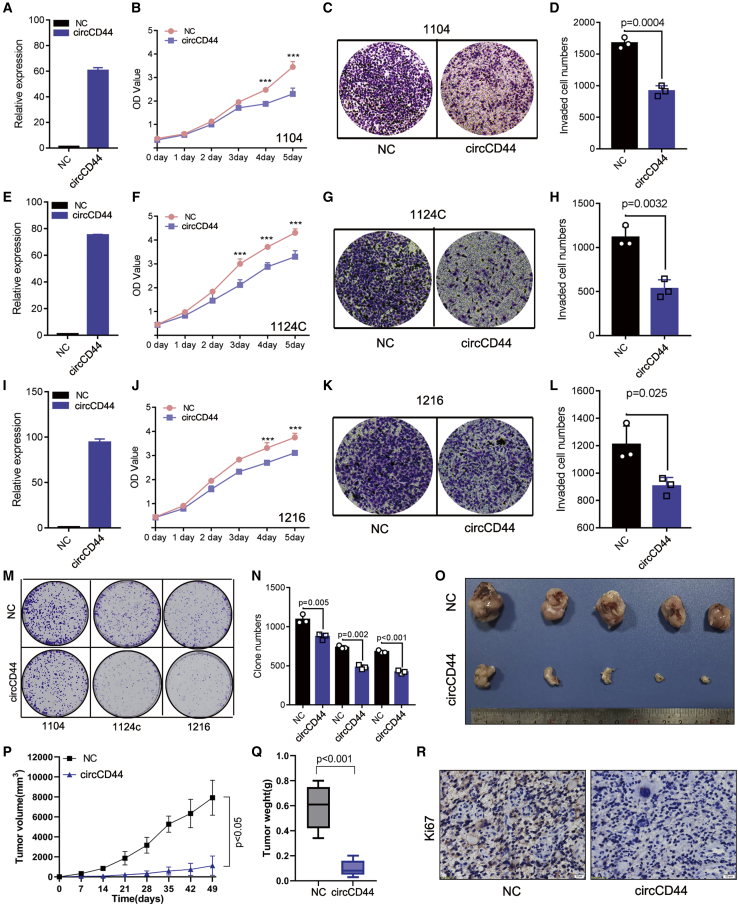
Figure 4.
circCD44 inhibits GBM cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo
(A, E, and I) Successful overexpression of circCD44 in 1104 (A), 1124C (E), and 1216 (I) cells was detected by RT-qPCR. (B, F, and J) The effect of ectopic circCD44 expression on 1104 (B), 1124C (F), and 1216 (J) cell proliferation was assessed with the CCK-8 cell growth assay. (C, G, and K) The effect of ectopic circCD44 expression on 1104 (C), 1124C (G), and 1216 (K) cell invasion was assessed with the transwell assay. (D, H, and L) Quantification of the number of invading cells from (C), (G), and (K). (D, H, and L) Quantification of the invading cells number from invasion assay of 1104 (D), 1124C (H), and 1216 cells (L). (M) Cell proliferation ability was evaluated by colony formation. (N) Quantification of the clone numbers of (M). (O) The representative tumor images in each group are displayed (n = 5). (P) Tumor volumes were measured and the growth curves were drawn. (Q) Tumor weight was analyzed. (R) Ki67 expression in each group was detected via IHC. Scale bar, 20 μm. ∗p<0.05; ∗∗p<0.01:∗∗∗p<0.001.