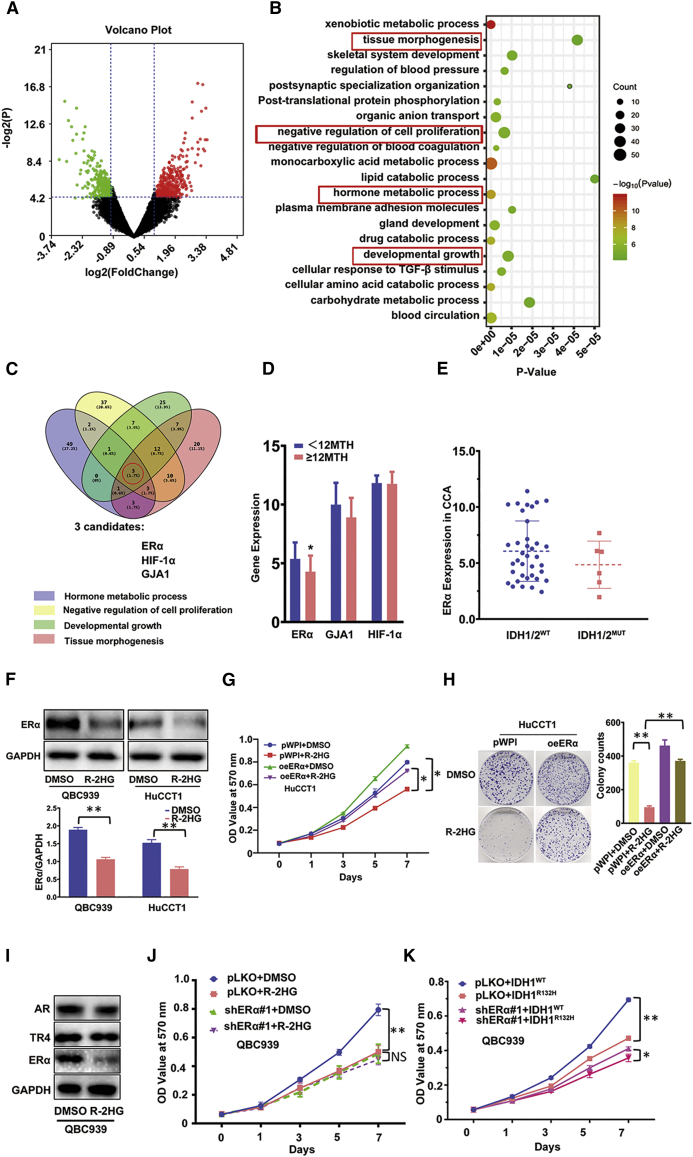
Figure 2.
ERα is involved in R-2HG suppression of CCA cell growth via decreasing ERα expression
(A) We extracted 738 differential genes from a microarray dataset (GEO: GSE107102). Red represents high overexpression, and green represents lower expression of ERα. (B) Top 20 enrichment pathways from the 738 differential genes. (C) ERα, HIF-1α, and GJA1 genes were obtained through overlapping the top four pathways of size related to proliferation. (D) According to overall survival (12 months [12MTH]), TCGA data was divided into two groups; then, we checked the differential expression of three genes (ERα, GJA1, and HIF-1α) between the two groups. (E) ERα expression comparing patients with IDH1/2WT versus mutant IDH1/2 (IDH1/2MUT). (F) Western blot was conducted to examine ERα expression between DMSO and R-2HG treatment in QBC939 and HuCCT1 cell lines. Quantitation in the lower panel. (G and H) Cell proliferation results of HuCCT1 cells transfected with/without (w/wo) oeERα (overexpressing ERα) and subsequently treated with DMSO or R-2HG are shown by an MTT assay (G) and sphere formation with quantitation at the right (H). (I) Western blot was used to detect AR, ERα, and TR4 expression in QBC939 cells treated with R-2HG. (J) QBC939 cells transfected w/wo shERα (knocked down ERα) and subsequently treated with DMSO or R-2HG, after which an MTT assay was performed to examine cell growth. (K) QBC939 cells transfected w/wo shERα and subsequently electro-transfected w/wo Cas9-IDH1-Puro+template, after which an MTT assay was performed to examine cell growth. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; NS, not significant.