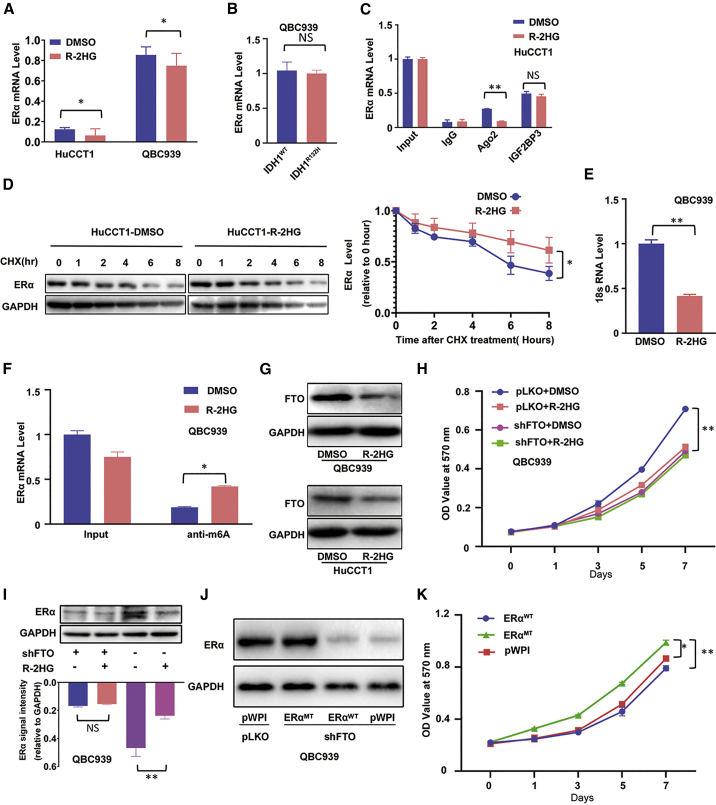
Figure 6.
R-2HG can suppress ERα expression via inducing high RNA-m6A methylation
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR was conducted to detect ERα mRNA expression in HuCCT1 cells and QBC939 cells treated with R-2HG. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR was conducted to detect ERα mRNA expression in QBC939 cells with/without (w/wo) IDH1R132H. (C) The ERα mRNA level was detected in the Ago2 complex and IGF2BP3 complex using a RIP assay in HuCCT1 cells treated with DMSO or R-2HG. (D) ERα protein stability test using cycloheximide (CHX) treatment in HuCCT1 cells treated w/wo R-2HG (left) and quantitation at the right. (E) Quantitative real-time PCR showed 18S rRNA levels in the ERα mRNA-biotin pull-down complex in QBC939 cells treated w/wo R-2HG. (F) The ERα mRNA level was detected in the anti-m6A complex using a RIP assay in QBC939 cells treated w/wo R-2HG. (G) FTO expression in QBC939 (upper) and HuCCT1 (lower) cells after R-2HG treatment. (H) QBC939 cells transfected w/wo shFTO and subsequently treated w/wo R-2HG, after which an MTT assay was performed to examine cell growth. (I) The methylation of ERα mRNA could change its protein expression. A western blot was used to examine ERα expression from the four groups as indicated in QBC939 cells (upper) with quantitation in the lower panel. (J) We knocked down FTO in QBC939 cells and then divided cells into three groups and transfected them with pWPI, oeERαWT, or mutant oeERα (oeERαMT). A western blot was used to detect ERα expression. (K) MTT assay was conducted to examine cell growth among the three groups as indicated in QBC939 cells. Quantitations are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; NS, not significant.