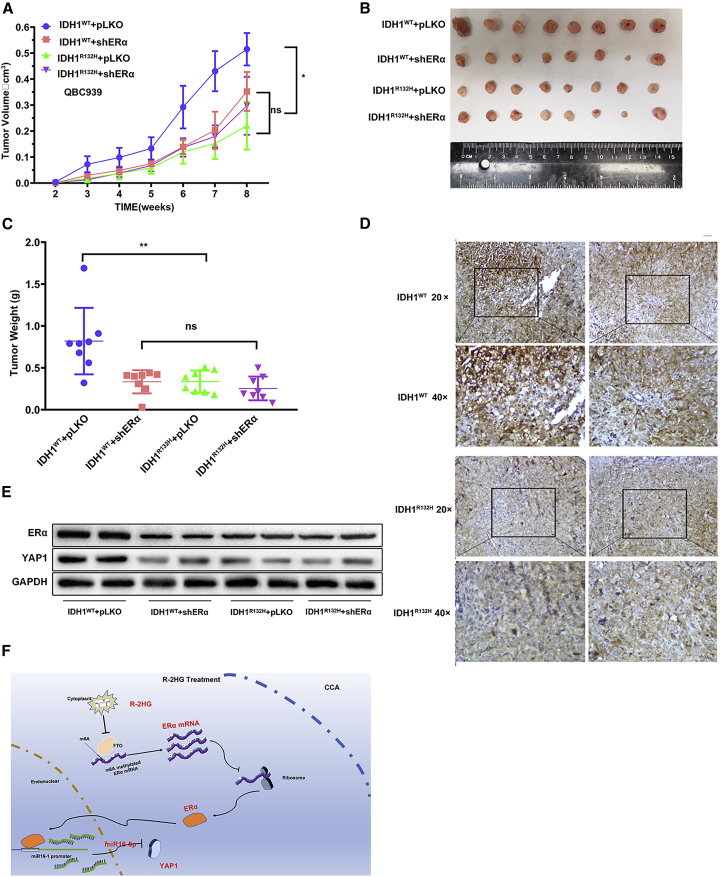
Figure 7.
In vivo mouse tumor model showing that the R-2HG-downregulated ERα signals could modulate tumor growth
(A) The QBC939 cells transfected with IDH1WT+pLKO, IDH1WT+shERα, IDH1R132H+pLKO, or IDH1R132H+shERα were subcutaneously implanted into female nude mice, and tumor sizes were measured weekly. After 8 weeks, the mice were sacrificed and the tumor growth rates of different groups were compared. (B) Gross comparison of CCA tumor size in the four groups of mice. (C) Quantification of tumor weights. (D) Representative images of the immunohistochemistry staining of YAP1 in each group. Brown signals indicate the positive YAP1 staining. (E) Two samples from each tumor group were randomly chosen to detect YAP1 and ERα using a western blot. (F) Schematic model of modulating the FTO/m6A methylated ERα/miR16-5p/YAP1 signaling by the oncometabolite R-2HG to suppress CCA growth. Quantitations are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; NS, not significant.