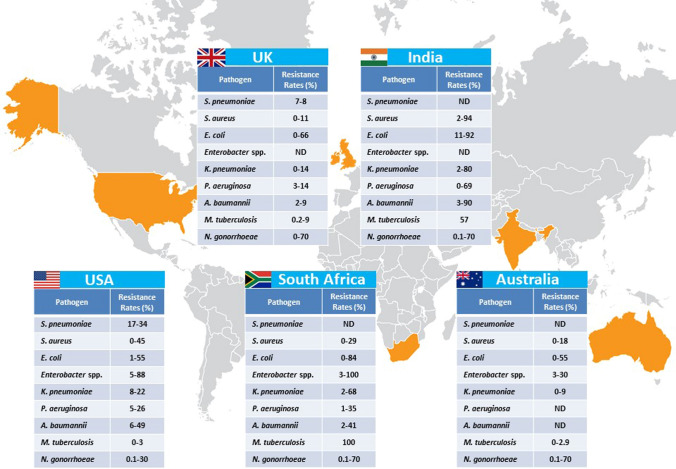
Fig. 2.
Antibiotic resistance levels associated with major bacterial pathogens across the globe. Data shown are from 2000 to 2014 and represent the percentage of isolates (the range) tested that are resistant to each antibiotic class used for each pathogen (pathogen specific), not taking into account the proportion of strains that are resistant to more than one antibiotic class. ROS: reactive oxygen species. For all pathogens except M. tuberculosis and N. gonorrhoeae, data were obtained from the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy (https://resistancemap.cddep.org). For M. tuberculosis, data were obtained from WHO Drug Resistant TB Surveillance & Response—Supplement: Global Tuberculosis Report 2014 (World Health Organization 2014a). For N. gonorrhoeae, data were obtained from the World Health Organization Global Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Program which covers strains analyzed between 2011 and 2014 (http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/rtis/gonococcal_resistance/en/). ND, no data provided. Copyright [Kathrin U. Jansen, William C. Gruber, Raphael Simon, James Wassil, and Annaliesa S. Anderson] 2021