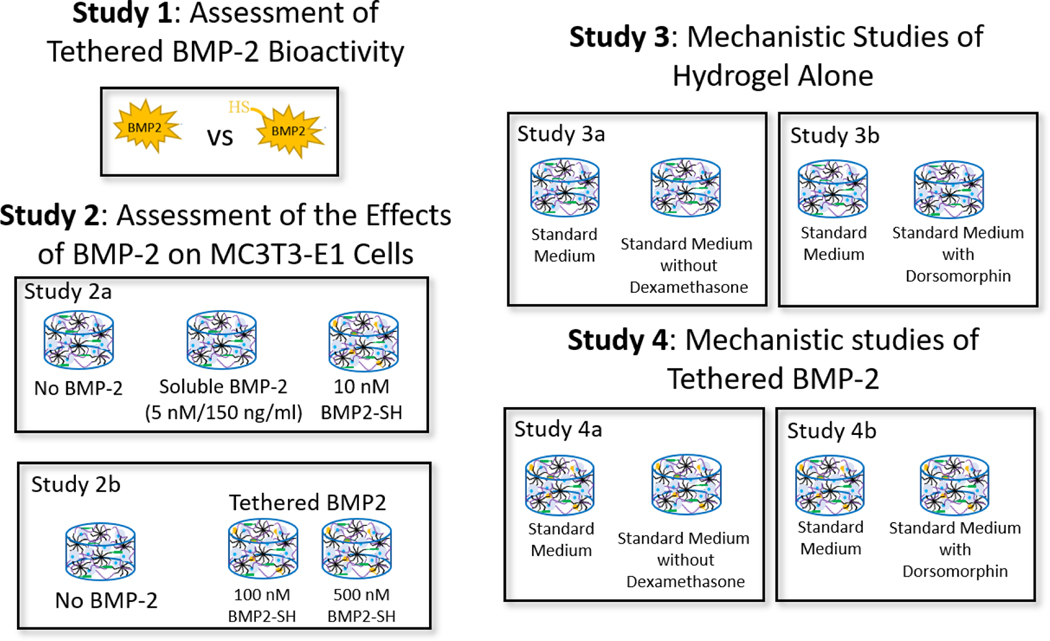
Figure 1.
An overview of the experimental design to assess the effectiveness of immobilizing BMP-2, via a thiol-norbornene click reaction, into PEG hydrogels. Study 1 assessed the bioactivity of thiolated BMP-2 in solution (study 1a) and the efficacy of tethering the functionalized growth factor to the PEG network (study 1b). A cell-reporter assay for SMAD 1/5/8 signaling and a modified-ELISA were used. Study 2 assessed the effects of BMP-2 (soluble and tethered) (study 2a) and concentration effects of tethered BMP-2 (study 2b) on MC3T3-E1 cells encapsulated in a PEG hydrogel and cultured in defined osteogenic medium (study 2a). Study 3 assessed the contribution of dexamethasone, which is present in the chemically defined medium (i.e., standard medium), on MC3T3-E1 cells encapsulated in the PEG hydrogel. The hydrogels were cultured in standard medium or standard medium without dexamethasone. Study 4 investigated if tethered BMP-2 signals via its receptors, that activates the SMAD 1/5/8 pathway, to induce the osteogenic response of the encapsulated cells. MC3T3-E1 cells were encapsulated in the PEG network and cultured in standard medium or standard medium with the inhibitor, dorsomorphin. In Studies 2–4, cell-laden hydrogels were cultured for up to seven days.