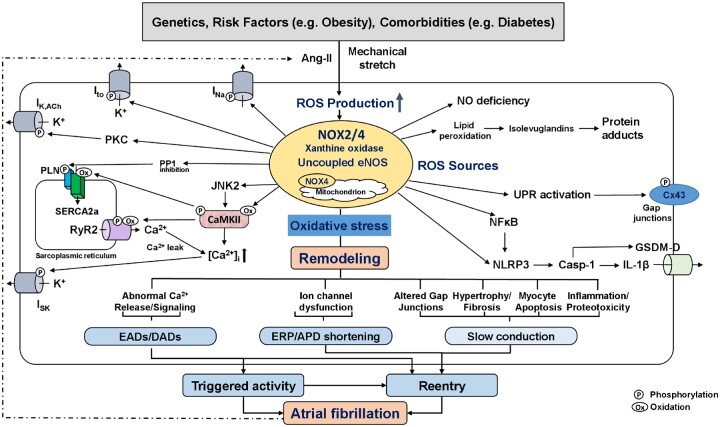
Figure 1.
Putative role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in atrial fibrillation (AF). ROS-production from activated NADPH-oxidase (NOX) isoforms, xanthine oxidase, and downstream ROS-generating systems including mitochondria and uncoupled eNOS. The sustained oxidative stress leads to abnormal Ca2+ signalling with potential occurrence of AF-triggering EADs and DADs, ion-channel dysfunction with ERP/APD-abbreviation, and to altered gap-junctions, fibrosis, myocyte apoptosis, and inflammation, which produce a heterogeneous slowing in impulse conduction. Shorter ERP and conduction slowing support the formation of AF-maintaining reentry. Examples of key mediators downstream of increased ROS-production include oxidized CaMKII (CaMKII), activated PKC, inhibited PP1, and activated NFkB and NLRP3-inflammasome. Activated CaMKII increases ryanodine-receptor type-2 (RyR2) hyperphospohrylation and causes sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-overload, both of which increases diastolic Ca2+-leak. NFkB is a redox-sensitive transcription factor that activates NLRP3-inflammatory signalling and causes structural remodelling by increasing the priming of NLRP3, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and matrix metalloproteinases. ROS-generation also increases lipid peroxidation and formation of highly reactive isolevuglandins that rapidly adduct and crosslink proteins causing myocyte proteotoxicity. AF further increases the activity of ROS-generating systems by increasing both angiotensin-II (Ang-II) and atrial stretch, creating a vicious cycle of atrial cardiomyopathy-driven NOX-activation and AF-mediated oxidative stress amplification, ultimately leading to AF-promoting atrial remodelling. APD, action-potential duration; CaMKII, Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II; Cx43, connexin-43; DAD, delayed afterdepolarization; EAD, early afterdepolarization; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide; ERP, effective refractory period; INa, Na+-current; ISK, small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+-current; Ito, transient-outward K+-current; JNK2, janus kinase-2; NFkB, nuclear-factor kappa-B; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin-domains containing protein-3; PKC, protein kinase-C; PP1, protein phosphatase type-1; UPR, unfolded protein response.