Table 2. Similarity Coefficientsa.
| name | measurement | range | reference(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Braun-Blanquet | x/max(y,z) | 0 to 1 | (53,54) | |
| Cosine | 0 to 1 | (55,56) | ||
| Dice | 0 to 1 | (57,58) | ||
| Dot-product | x | 0 to ∞ | N/A | |
| Euclidean | 0 to 1 | N/A | ||
| Kulczynski | 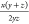 |
0 to 1 | (59) | |
| McConnaughey | –1 to 1 | (60) | ||
| Russel/Rao | x/w | 0 to 1 | (61) | |
| Simpson | x/min(y,z) | 0 to 1 | (62) | |
| Sokal/Sneath | 0 to 1 | (63) | ||
| Tanimoto | 0 to 1 | (64,65) | ||
| Tullos | XYZ | 0 to 1 | (66) | |
| Tversky | 0 to 1 | (67) |
A total of 13 different similarity
coefficients (several of these coefficients were collected by Raymond
and Willett)52 were compiled for measuring
the degree of structural similarity of two compounds described by
a given molecular fingerprint encoding. Here, x is
the number of bits set in both fingerprints, y is
the number of bits set in the first fingerprint, z is the number of bits set in the second fingerprint, and w is the
total number of bits in the bit string. For the Tullos similarity
coefficient, 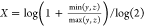 ,
, 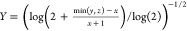 , and
, and 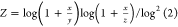 . For the asymmetric
evaluation of the Tversky
similarity coefficient, α = 0.9. Here, we assume that the parameters
of the Tversky coefficient in its original formulation,
. For the asymmetric
evaluation of the Tversky
similarity coefficient, α = 0.9. Here, we assume that the parameters
of the Tversky coefficient in its original formulation, 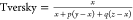 , will follow p + q = 1. The Dice and Tanimoto similarity
coefficients are
two symmetric instances of the Tversky coefficient, where p = q = 0.5 and p = q = 1, respectively.
, will follow p + q = 1. The Dice and Tanimoto similarity
coefficients are
two symmetric instances of the Tversky coefficient, where p = q = 0.5 and p = q = 1, respectively.
