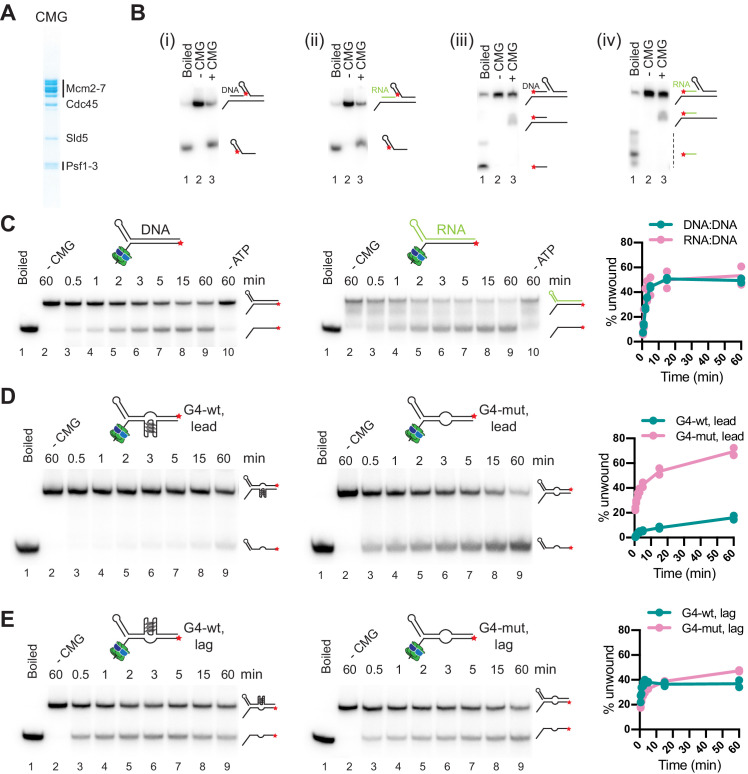
Figure 5. CMG can unwind or translocate on RNA:DNA hybrids, while G-quadruplexes (G4s) can block DNA unwinding by CMG.
(A) Purified CMG. (B) Helicase assays with 40 bp forked DNA duplex preceded by 40 bp DNA (i + iii) or RNA:DNA (ii + iv) duplex. ★ indicates position of 5’-32 P label. Products were analyzed by native PAGE and autoradiography. (C) CMG helicase activity on 60 bp forked DNA (left) or RNA:DNA duplex (right). Plot shows average of two replicates. (D) CMG helicase activity on 60 bp substrate harboring wildtype (left) or mutant (right) G4 sequence on the template strand (‘lead’). (E) As (D), with wildtype (left) or mutant (right) G4 sequence on the non-template strand (‘lag’).