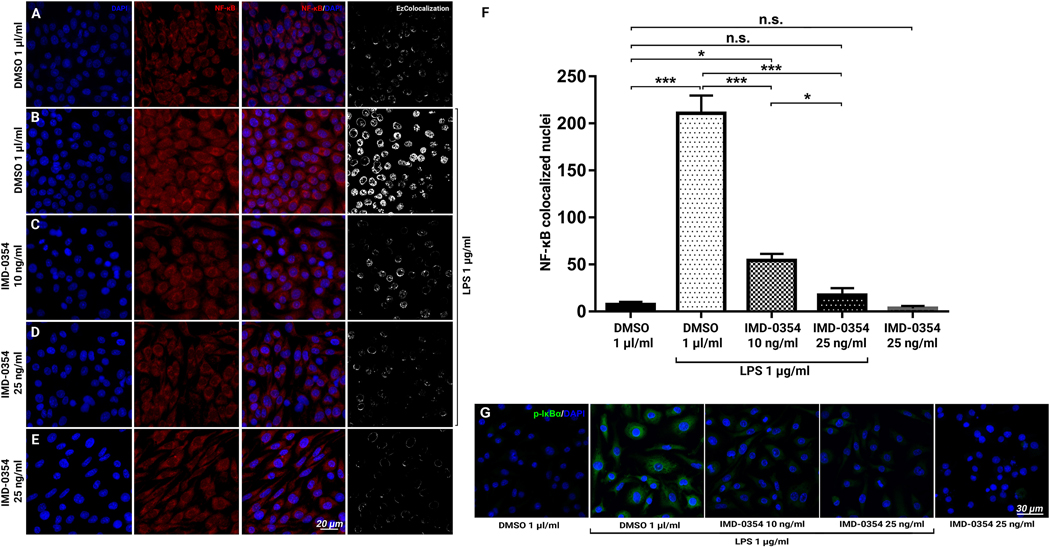
Figure 5:
Effect of IMD-0354 treatment on NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation in LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells.
Inhibitory effect of IMD-0354 (10 ng/ml) on NF-κB (red) nuclear translocation in BV-2 cell cultures. DMSO (1 μl/ml)-treated control, cell nuclei counterstained with DAPI (A), LPS 1 μg/ml-stimulated BV-2 cells (B), 10 ng/ml IMD-0354 (C) and 25 ng/ml IMD-0354 (D) with 1 μg/ml LPS stiumulation, demonstrate dose-dependent reduction in nuclear localization of NF-κB. (E) IMD-0354 treatment 25 ng/ml without LPS stimulation. (F) Quantitative analysis of NF-κB nuclear translocation cells. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. n = 10 (F) p-IκBα Immunofluorescent staining in BV-2 cells treated with DMSO (1 μl/ml), LPS 1 μg/ml-stimulated, 10 ng/ml, 25 ng/ml IMD-0354 with 1 μg/ml LPS stimulation and IMD-0354 treatment 25 ng/ml without LPS stimulation.