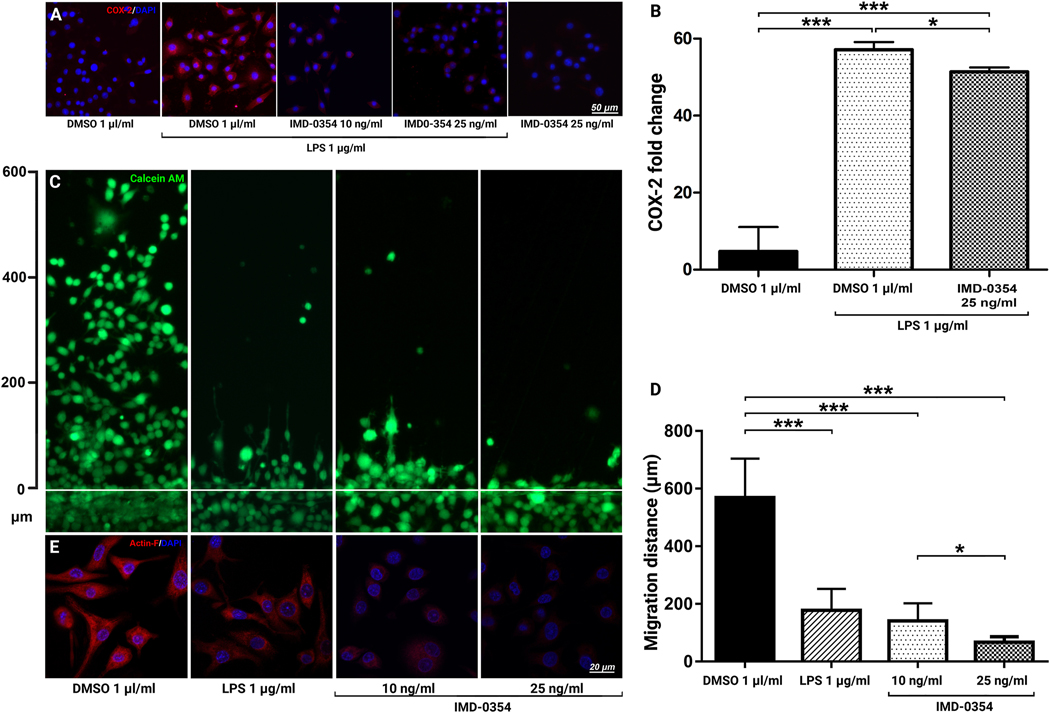
Figure 6:
Effects of IKK2 Inhibition on BV-2 cell activation and motility.
COX-2 expression in LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells treated with IKK2 inhibitor IMD-0354 (A). Quantitative qRT-PCR analysis of COX-2 expression (n = 3) (B). Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of IMD-0354 (10 and 25 ng/ml) on BV-2 cell migration relative to control (1 μl/ml DMSO. Live culture images of BV-2 cells scratch (wound healing) assay cultures treated with DMSO 1 μl/ml, LPS 1 μg/ml, IMD-0354 (10 and 25 ng/ml) 24-hours after induction of the scratch and treatment. BV-2 cells were visualized with Calcein-AM (green) (C). Quantification of BV-2 cells migration distance (n = 8) (D). BV-2 cells F-actin expression and cytoskeletal arrangement in control, LPS 1 μg/ml, IMD-0354 (10 and 25 ng/ml) (E). IKK2 Inhibition decreased expression and organization of F-actin filaments in a dose-dependent manner resulting in rounded cell morphology. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.