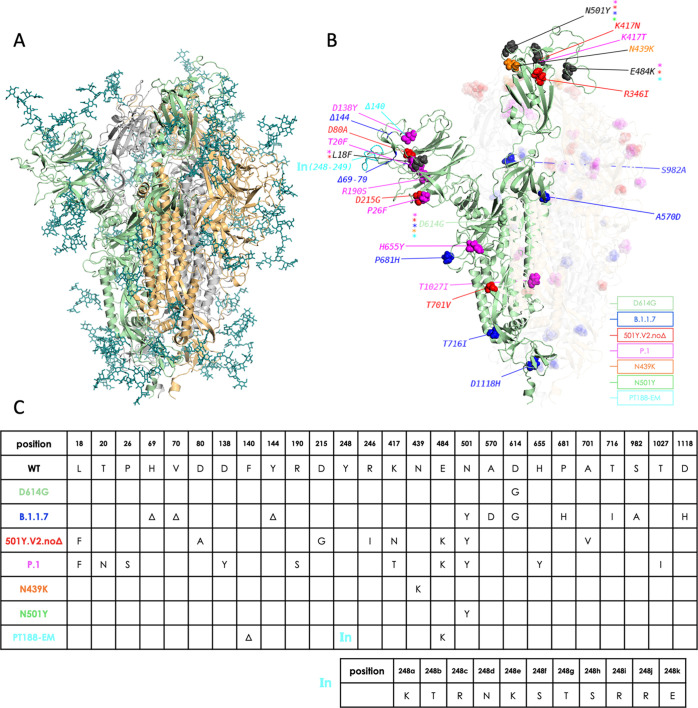
Figure 1.
Overview of simulated variants (definitions in main text). (A) The full-length, fully glycosylated trimeric structure corresponding to pdb code 6VSB. Protomer A (RBD “up”): secondary structure in green; protomers B and C (RBD “down”): grey and sand, respectively. Glycans’ C, N, and O atoms rendered as teal sticks. (B) Positions and nature of mutations highlighted on protomer A of different variants. Mutant residues’ heavy atoms are rendered as spheres; a different color is assigned to each variant, as indicated in the legend. Mutations common to more than one variant are rendered and/or labeled in black, with colored asterisks denoting variants carrying the mutation. The insertion in the PT188-EM variant (cyan) is denoted by “In(248–249)”. Protomers B and C are also shown with their respective mutations, but rendered with increased transparency for clarity; glycans are omitted; (C) synopsis of mutations on the different variants simulated in this work, including the 11-residue insertion in the PT188-EM variant.