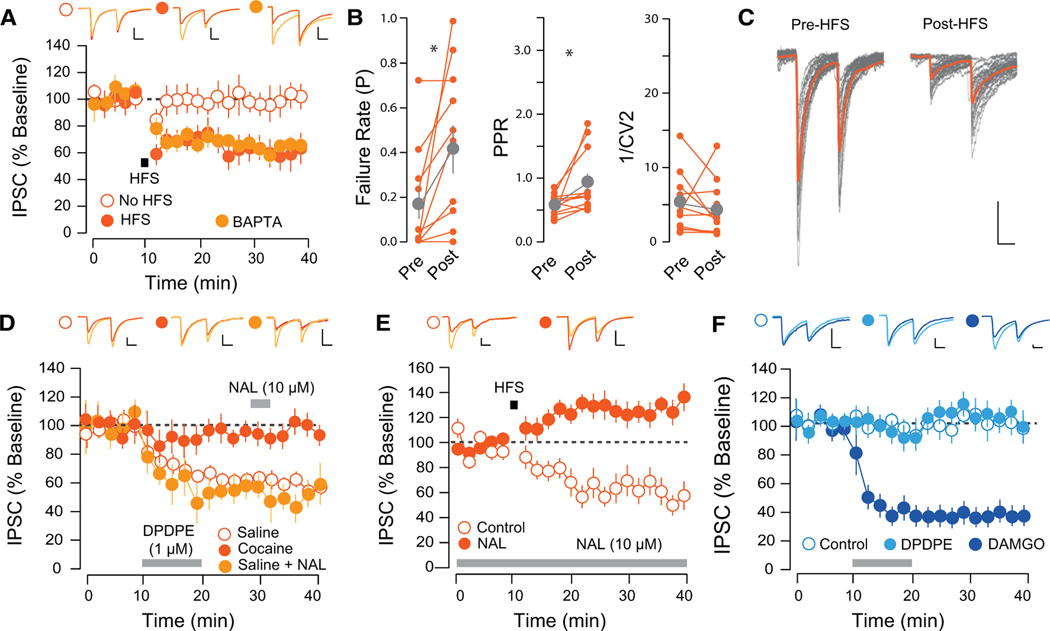
Figure 4. HFS-Induced LTD at D2-VP Synapses Is Presynaptic and DOR Mediated.
(A) HFS-induced LTD at D2-VP synapses was insensitive to postsynaptic BAPTA (CTRL, 103.54% ± 17.57%, 5 cells from 2 mice; HFS, 61.43% ± 9.92%, 10 cells from 4 mice; HFS with BAPTA, 60.62% ± 6.42%, 6 slices from 3 mice).
(B) HFS-LTD was associated with an increase in the PPR and failure rate and a decrease in C1/V12 (paired t test PPR, t = 2.45, p = 0.035; FR, t = 2.79, p = 0.019; 1/CV2, t = 1.079, p = 0.306, 11 cells from 6 mice).
(C) Twenty individual IPSC traces pre- and post-HFS protocol.
(D) DPDPE induced an LTD in saline-, but not cocaine-treated, mice (SAL, 59.33% ± 7.12%, 10 cells from 3 mice; COC, 97.994% ± 8.14%, 8 cells from 3 mice). Naltrindole (NAL) applied after DPDPE-LTD did not reverse the plasticity (52.92% ± 8.5%, 5 cells from 2 mice).
(E) Incubation in NAL prevented the HFS-induced LTD (CTRL, 61.43% ± 9.92%, 10 cells from 4 mice; NAL, 130.4% ± 8.84%, 9 cells from 5 mice).
(F) DPDPE did not affect transmission at D1-VP synapses (CTRL, 111.85% ± 18.49%, 3 cells from 3 mice; DPDE, 106.99% ± 6.49%, 11 cells from 4 mice); DAMGO (1 μM) induced a depression of IPSCs (61.33% ± 6.08%, 6 cells from 3 mice).
*p < 0.05, all plots mean ± SEM. For representative traces, first and last 20 trials of recording in light and dark orange, respectively. Scale bars, 20 pA, 20 ms. Related to Figure S4.