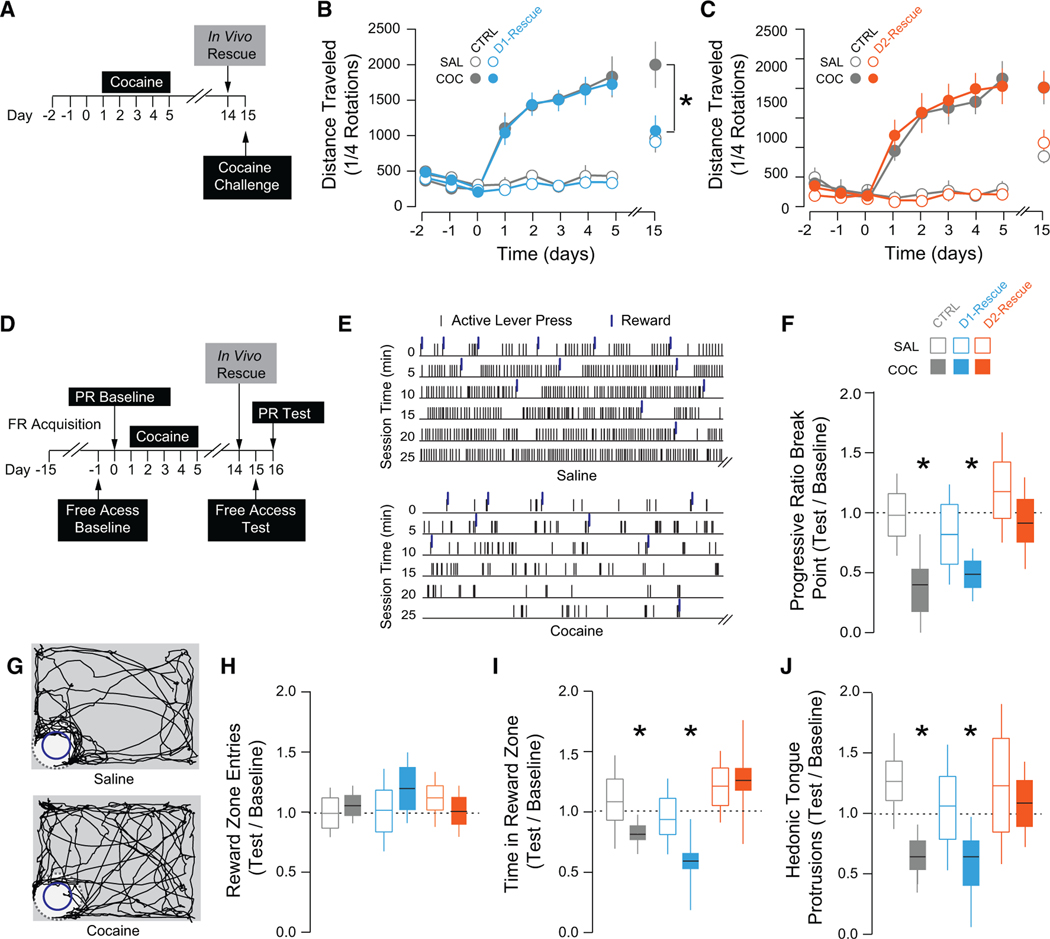
Figure 6. Selectively Normalizing Transmission at D1- or D2-MSN-to-VP Synapses Differentially Affects Drug-Adaptive Behavior.
(A–C) Locomotor sensitization experiments.
(A) Schematic of experiment.
(B) In vivo rescue of D1 transmission abolished the sensitized response to cocaine (COC CTRL, 1,578.0 ± 248.8, n = 7; COC with D1 rescue, 1,026.1 ± 133.08,n = 12; t = 2.087, p = 0.05), but had no effect on acute response to cocaine (SAL CTRL, 878.83 ± 227.41, n = 6; SAL with D1 rescue, 860.3 ± 134.6, n = 8; t = 0.07, p = 0.94).
(C) Rescue of D2-MSN VP transmission had no effect on cocaine response (COC CTRL, 1,735.86 ± 281.74, n = 7; COC with D2 rescue, 1,513.58 ± 161.20, n = 12; t = 0.21, p = 0.83; SAL CTRL, 1,042.17 ± 151.81, n = 6; SAL with D2 rescue, 1,151.25 ± 66.55, n = 8; t = 0.70, p = 0.50).
(D) Schematic of sucrose-related experiments.
(E and F) Operant task (E) raster plots of first 30 min of PR test in saline- (top) and cocaine-treated mouse (bottom). (F) Cocaine-treated mice had lower break points during the test relative to baseline (SAL CTRL, 1.10 ± 0.17, n = 9, t = 0.594, p = 0.56; COC CTRL, 0.597 ± 0.18, n = 14, t = 2.24, p = 0.034) and performance was impaired in cocaine-treated mice following D1 rescue (0.49 ± 0.06, n = 8, t = 8.67, p < 0.001), while D2 rescue normalized the break point (1.05 ± 0.18, n = 9, t = 0.26, p = 0.801).
(G–J) Free access task (G) track plots of a saline- (top) and cocaine-treated mouse (bottom) during the free access task. (H) There was no effect of cocaine or intervention on reward zone entries. (I) Cocaine-treated mice spent less time in the reward zone during the test relative to baseline (SAL CTRL, 1.00 ± 0.097, n = 9, t = 0.01, p = 0.99; COC CTRL, 0.79 ± 0.06, n = 14, t = 3.47, p = 0.002) and performance was impaired following D1 rescue (SAL, 0.72 ± 0.11, n = 6, t = 2.47, p = 0.032; COC, 0.65 ± 0.13, n = 8, t = 2.69, p = 0.0176), while D2 rescue normalized the break point in cocaine-treated mice (1.07 ± 0.18, n = 9, t = 0.38, p = 0.71).
(J) Hedonic tongue protrusions were reduced relative to baseline in cocaine-treated mice (0.582 ± 0.091, n = 14, t = 4.59, p < 0.001) and mice that had D1 rescue protocol (0.627 ± 0.15, n = 8, t = 2.85, p = 0.013); mice with the D2 rescue protocol were not impaired relative to baseline (0.92 ± 0.22, n = 9, t = 0.36, p = 0.727). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by t test comparing locomotor response to cocaine challenge (B and C) or normalized response to null hypothesis (F and H–J). All plots are mean ± SEM. Related to Figures S5–S8 and Table S1.