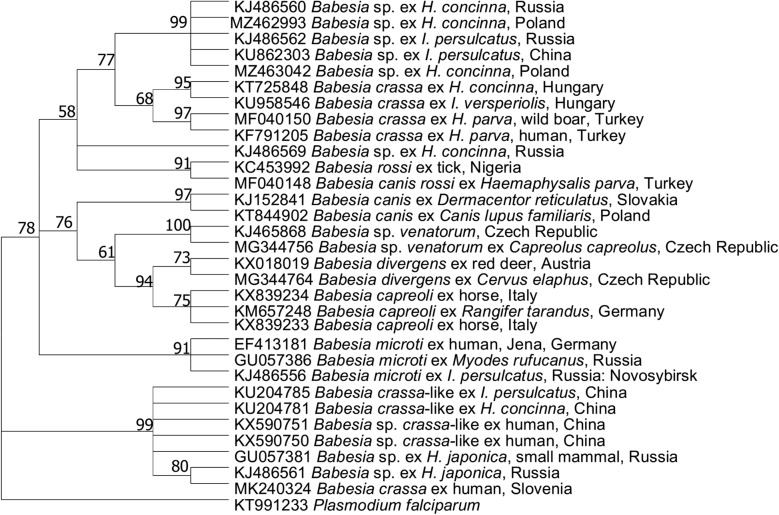
Fig. 2.
Molecular phylogenetic analysis of 18S rDNA of selected Babesia spp. (550 base pairs). The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum likelihood method and the Kimura two-parameter model. The tree with the highest log likelihood (− 2752,03) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying neighbour-joining and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the maximum composite likelihood approach, and then selecting the topology with a superior log likelihood value. A discrete γ distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites [five categories (+ G, parameter = 2,1600)]. This analysis involved 32 nucleotide sequences. There were a total of 458 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X