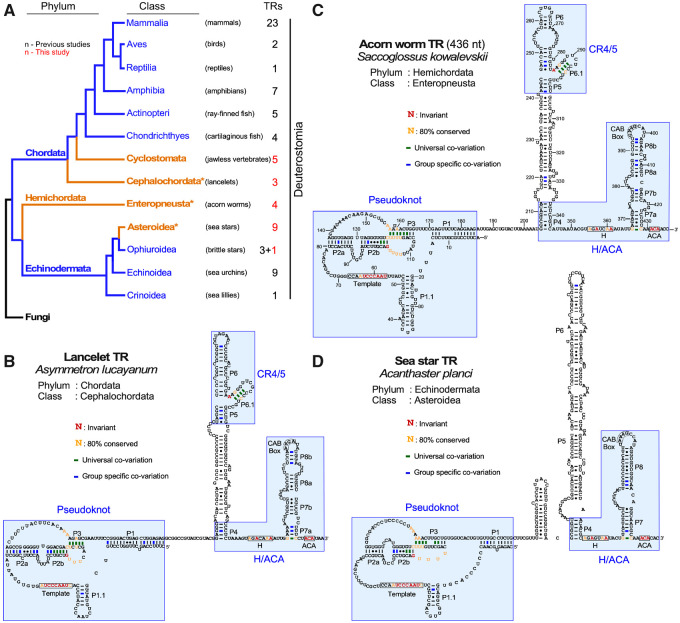
Fig. 2.
Secondary structures of deuterostome TRs. (A) Evolutionary relationship of deuterostome phyla and classes with TR identified. The numbers of TRs identified in this and previous studies for each class are indicated. An asterisk denotes the classes for which the TR secondary structure of a representative species is shown in B–D. Fungi represents the outgroup in the phylogenetic tree. (B–D) Representative TR secondary structures determined by phylogenetic comparative sequence analyses are shown for Asymmetron lucayanum (lancelet) from phylum chordata (B), Saccoglossus kowalevskii (acorn worm) from phylum hemichordata (C), and Acanthaster planci (sea star) from phylum Echinodermata (D). The conserved TR structural domains are shaded in blue. Universal covariations (thick lines), invariant residues, and residues with >80% conservation are based on the sequence alignment of 55 previously identified animal TRs and 82 novel metazoan TRs identified in this study. Group-specific covariations (thick lines) are indicated and based on the sequence alignment of TRs from individual groups including 50 chordate TRs (42 previously identified and eight novel), 23 echinoderm (13 previously identified and ten novel), and four acorn worm TRs.