Figure 2.
Identification of chromatin-bound FOXC1 interacting proteins
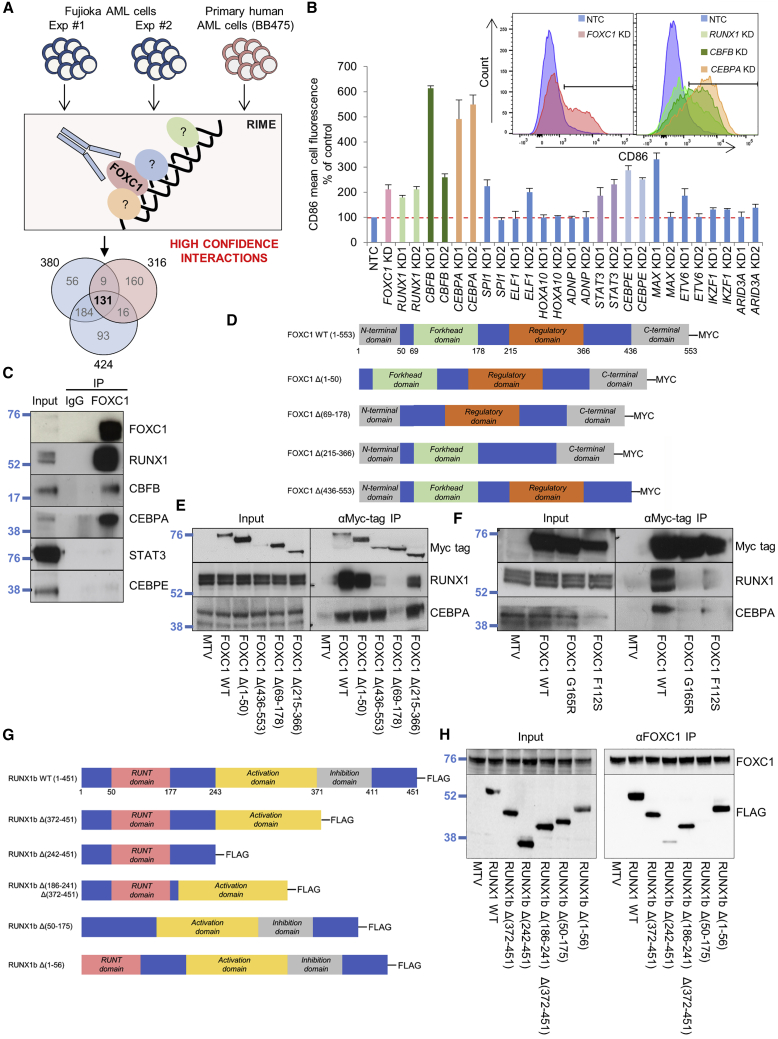
(A) Experimental outline.
(B) Human Fujioka AML cells were infected with lentiviruses targeting the indicated genes for KD or a NTC. Bar chart shows mean + SEM CD86 mean cell fluorescence on day 5 (n = 3). Embedded panel: representative flow cytometry plots.
(C) Anti-FOXC1 immunoprecipitation (IP) in Fujioka AML cells (representative of n = 3).
(D–F) Fujioka AML cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing coding sequences for full-length or domain mutant versions of FOXC1. (D) FOXC1 and domain mutants used. (E and F) Western blots show expression of the indicated proteins in the indicated conditions in coimmunoprecipitation (coIP) experiments (representative of n = 3).
(G and H) 293 cells were transfected with vectors expressing coding sequences for full-length or domain mutant versions of RUNX1b. (G) RUNX1b and domain mutants used. (H) Western blots show expression of the indicated proteins in the indicated conditions in coIP experiments (representative of n = 2).
See also Figure S2.