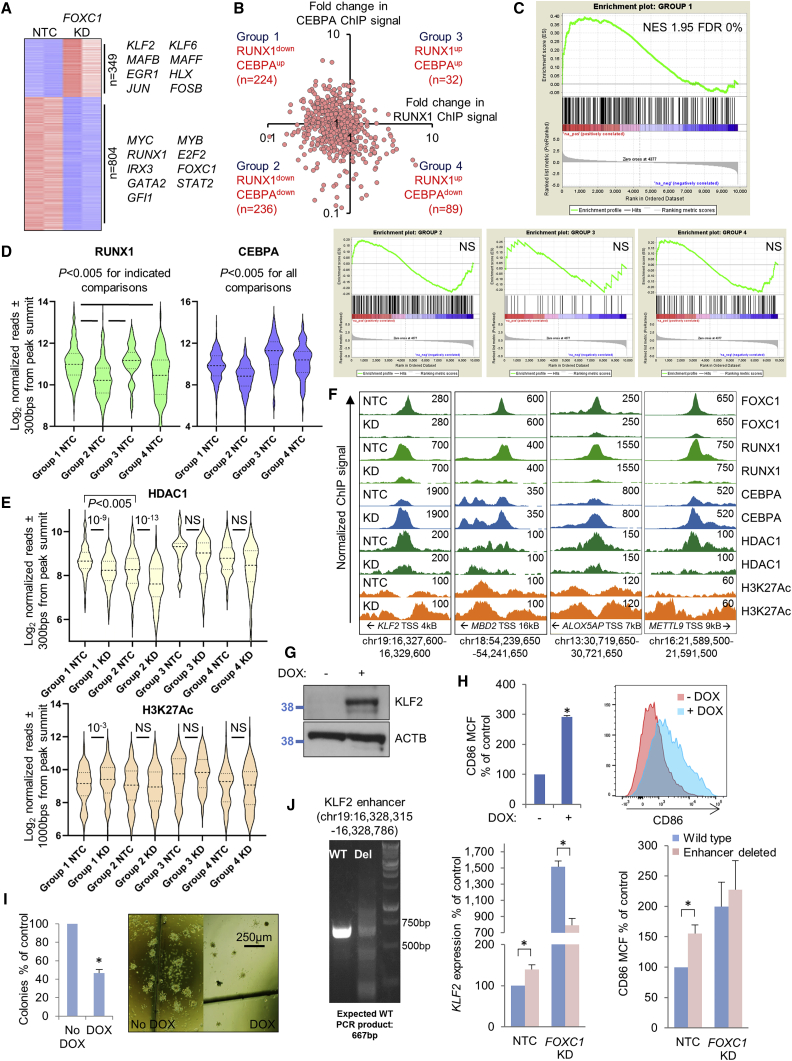
Figure 5.
Reduced RUNX1 and increased CEBPA ChIP signal at enhancers controlling differentiation genes after FOXC1 KD
(A–F) Human Fujioka AML cells were infected with a lentivirus targeting FOXC1 for KD or an NTC. (A) Heatmap shows differentially expressed genes on day 4 after KD initiation; transcription factor genes are highlighted. (B) Dot plot shows fold change in relative ChIP signal at 581 FR-20 enhancer sites and definition of four sub-groups. (C) GSEA plots. (D and E) Violin plots show distribution, median (thick dotted line), and interquartile range (light dotted lines) for ChIP signal for the indicated proteins and the indicated groups of FR-20 enhancer sites in control (NTC) or FOXC1 KD cells on day 5. p value, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc or unpaired t test. (F) Exemplar ChIP-seq tracks.
(G–I) Fujioka cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing KLF2 under the control of a doxycycline-regulated promoter. (G) Western blot shows induced expression of KLF2. (H) Bar chart (left panel) shows mean + SEM mean cell fluorescence (MCF) for CD86 (n = 3). Right panel: representative flow cytometry plots. (I) Bar chart (left panel) shows means + SEM CFC frequencies of KLF2-expressing Fujioka cells relative to control cells after 10 days in semi-solid culture (n = 3). Right panel: representative colonies.
(J) CRISPR deletion of a KLF2 regulatory element (left panel) and bar charts showing mean + SEM KLF2 expression relative to ACTB as determined by qPCR (middle panel) and CD86 cell fluorescence (right panel) on day 4 after KD initiation (n = 3; ∗p < 0.05 by unpaired t test).
FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score. See also Figure S5.