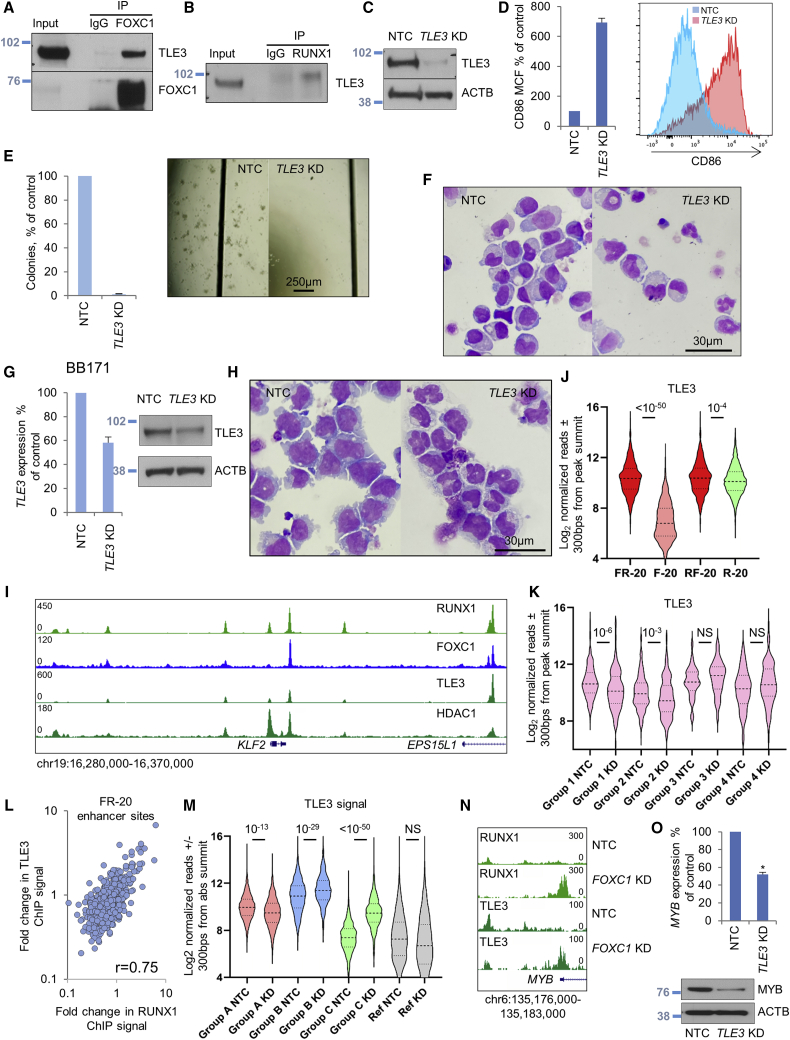
Figure 7.
FOXC1 stabilizes TLE3 and RUNX1 binding at enhancers controlling differentiation
(A and B) Western blots (representative of n = 3) show the indicated IPs from Fujioka cell lysates.
(C–F) Fujioka AML cells were infected with a lentivirus targeting TLE3 for KD or an NTC. (C) Western blot. (D) Bar chart (left panel) shows mean + SEM CD86 mean cell fluorescence (n = 3). Right panel: representative flow cytometry plots. (E) Bar chart (left panel) shows the mean + SEM CFC frequencies for TLE3 KD cells relative to control cells enumerated after 12 days (n = 3). Right panel: representative colonies. (F) Cytospins from (D).
(G and H) Primary patient AML cells (BB171) were infected with lentiviral vectors targeting TLE3 for KD or an NTC. (G) Transcript and protein KD. (H) Cytospins from day 12 after KD initiation.
(I) Exemplar ChIP-seq tracks.
(J) Violin plot shows distribution, median (thick dotted line), and interquartile range (light dotted lines) for TLE3 ChIP signal at the indicated sites in control (NTC) Fujioka AML cells. p value, unpaired t test.
(K) Violin plot shows TLE3 ChIP signal at the indicated FR-20 enhancer sites in control and FOXC1 KD Fujioka cells. p values, unpaired t test.
(L) Dot plot shows fold change in relative TLE3 and RUNX1 ChIP signal at each of 581 FR-20 enhancer sites.
(M) Violin plot shows TLE3 ChIP signal at the indicated RUNX1 group binding sites in control and FOXC1 KD Fujioka cells. p values, unpaired t test.
(N) Exemplar ChIP-seq tracks.
(O) Bar chart (top panel) shows mean + SEM MYB expression relative to ACTB (qPCR). Bottom panel: western blot.
See also Figure S7.