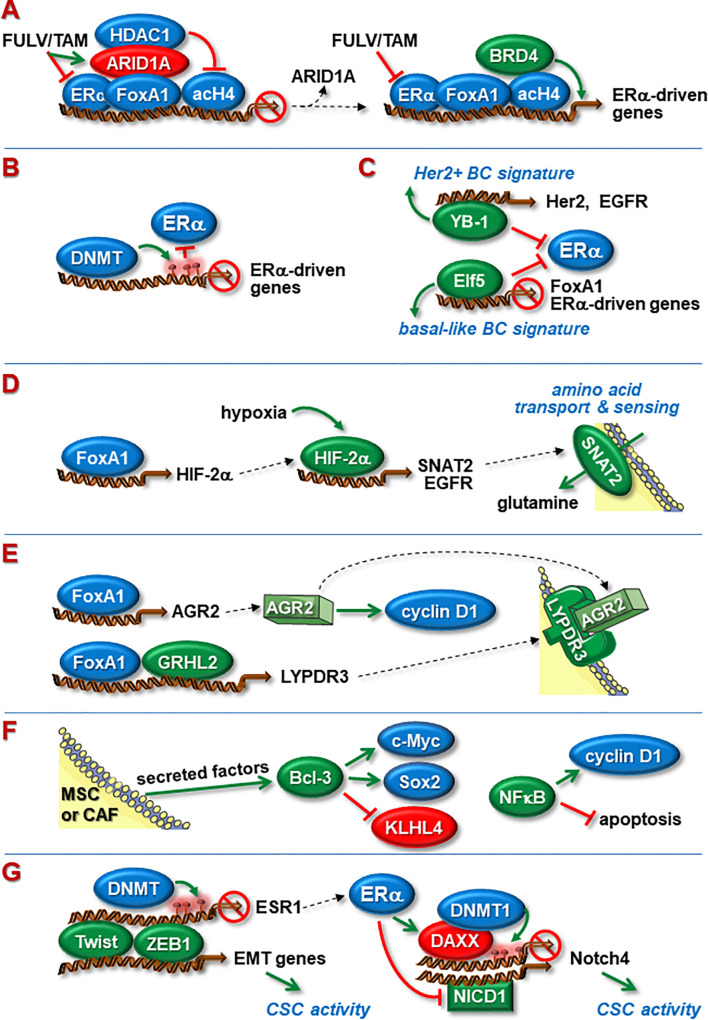
Figure 2.
Nuclear proteins involved in ENDO-R. (A) Blockage of ERα function by FULV or TAM causes ARID1A to bind to FoxA1 leading to transcriptional inhibition of ERα-driven genes by recruitment of HDAC1. Dysfunctional ARID1A leads to higher abundance of acetylated histone 4 (acH4) and recruitment of BRD4, able to active transcription despite the presence of anti-estrogens. (B) ENDO-R often coincides with DNMT-mediated DNA methylation of ERα-driven genes at promoters and/or enhancers, resulting in blockage of ERα binding to these sites. (C) Acquisition of ENDO-R by transcriptionally re-programming cells. YB-1 suppresses ERα activity and upregulates the expression of Her2 and EGFR leading to a Her2-driven transcriptional pattern. Elf-5 inhibits the expression of ERα and FoxA1 and fosters a transcriptional pattern typically seen in basal-like breast cancer. (D) Hypoxia promotes ENDO-R by activating HIFs. FoxA1-regulated HIF-2α stimulates the transcription of EGFR and SNAT2, the latter being a transmembrane transporter and sensor of amino acids. Anti-estrogen resistant cells may use SNAT2-imported glutamine as a major carbohydrate source to maintain metabolism. (E) Independent of ERα, FoxA1 can stimulate the transcription of AGR2 and, in cooperation with GRHL2, the transcription of LYPDR3. AGR2 can cause the cyclin D1 synthesis to rise. FoxA1, GRHL2, LYPDR3 and AGR2 may act in concert to induce ENDO-R. (F) Members of the NFкB/Iк;B family may be involved in ENDO-R. NFкB supports ENDO-R by stimulating cyclin D1 expression and by inhibiting apoptosis. Bcl-3, whose expression in BCs is induced by MSC- and CAF-secreted factors, causes higher expression of proliferation-stimulatory c-Myc and anti-apoptotic stem cell factor Sox2 and blocks proliferation-inhibitory KLHL4. (G) Twist and ZEB1 can enhance CSC activity by inducing EMT. Additionally, Twist and ZEB1 can suppress ERα expression by recruiting DNMT to the esr1 promoter. ERα may limit CSC activity by suppressing the transcription of Notch4. One way involves induced expression of the transcriptional repressor DAXX followed by DNMT1-dependent methylation, another down-regulated abundance of Notch1-derived NICD1, a positive regulator of Notch4 transcription. Green and red ovals indicate proteins that promote or inhibit anti-estrogen resistance, respectively. Green arrows indicate a positive, red T-shaped symbols a blocking effect. Red circles denote CpG methylations.