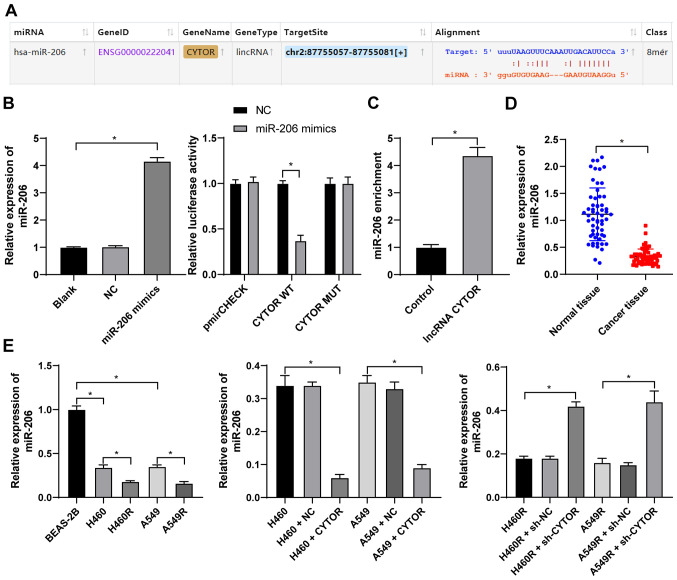
Figure 6.
CYTOR targets miR-206. (A) The binding site between CYTOR and miR-206 predicted via starBase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/). (B) The transfection of miR-206 mimics was confirmed by RT-qPCR and the binding association between CYTOR and miR-206 was verified by a dual-luciferase reporter assay. (C) The binding relationship between CYTOR and miR-206 in H460 cells was confirmed by an RNA pull-down assay. (D and E) miR-206 expression in (D) patients with NSCLC and (E) NSCLC cell lines as detected by RT-qPCR. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Cell experiments were performed as three repeats. *P<0.05. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; CYTOR, long noncoding RNA cytoskeleton regulator; NC, negative control; CYTOR, long noncoding RNA cytoskeleton regulator; sh-CYTOR, short hairpin RNA targeting CYTOR; A549R, A549 with radioresistance; miR/miRNA, microRNA; lincRNA, long intergenic non-coding RNA; WT, wild-type; MUT, mutant; hsa, Homo sapiens.