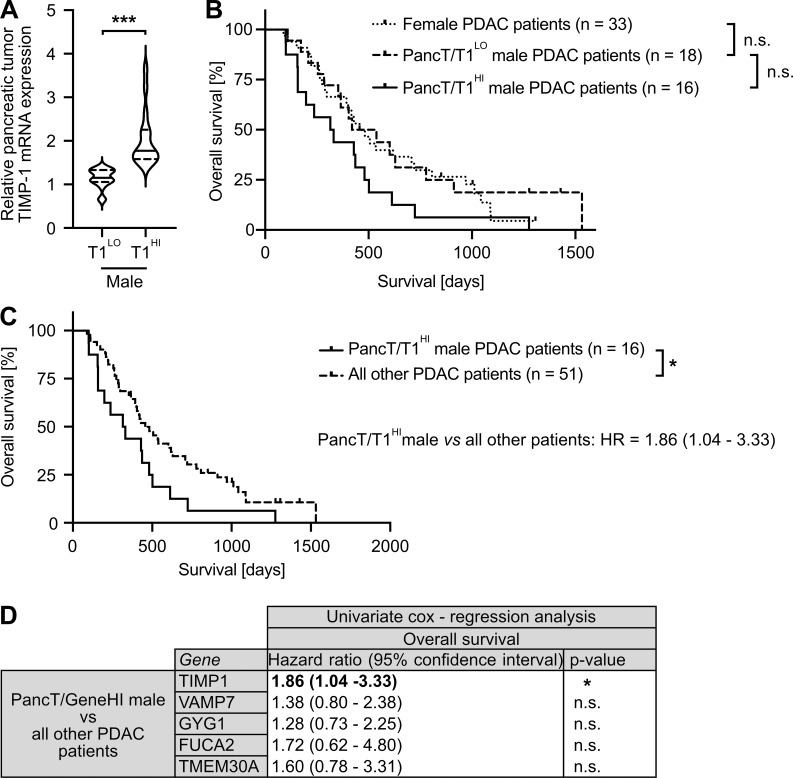
Figure 5.
Identification of a subpopulation of male PDAC patients with increased TIMP1 expression in PancTs accounting for sex differences in PDAC survival. (A) TIMP1 mRNA expression in the pancreatic primary tumors of male PDAC patients separated by two-step cluster analysis into males with low (T1LO; n = 18) or high (T1HI; n = 16) TIMP1 expression. Student’s t test was employed for statistics. (B) Probability of overall survival of female (n = 33) or male PDAC patients with low (PancT/T1LO; n = 18) or high (PancT/T1HI; n = 16) TIMP1 mRNA expression in pancreatic primary tumors. Log-rank statistics were employed for statistics. The difference in overall survival between PancT/T1LO and PancT/T1HI male PDAC patients was close to significant (P = 0.052). (C) Probability of overall survival of male PDAC patients with high TIMP1 mRNA expression in the pancreatic primary tumor (PancT/T1HI; n = 16) compared with all other patients (n = 51). Log-rank statistics were employed for statistics. HRs with 95% confidence intervals were determined by Cox regression analysis between PancT/T1HI males and all other PDAC patients. (D) HRs with 95% confidence intervals for overall survival between a subpopulation of male PDAC patients with increased expression of TIMP1, VAMP7, GYG1, FUCA1, or TMEM30A (determined by two-step cluster analysis) and all other PDAC patients, respectively. Cox regression analysis was employed for statistics. *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001 (A–D).