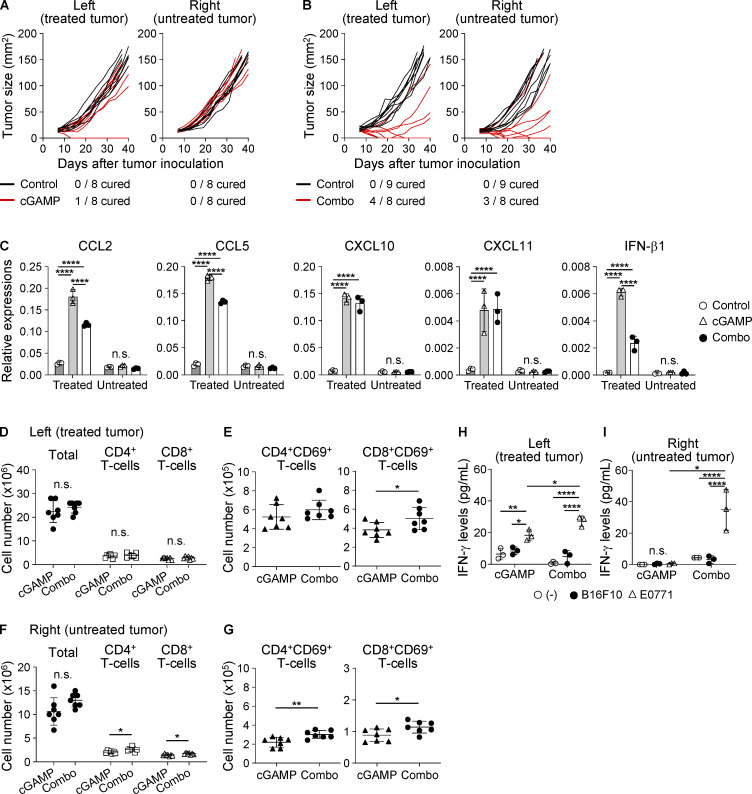
Figure S4.
Combination therapy with cGAMP and anti-CD47 mAb enhances systemic anti-tumor immunity. WT mice were inoculated with E0771 cells in both left and right mammary fat pads and treated with control, cGAMP, or combination therapy in only the left tumor tissue on day 7. (A and B) Individual tumor sizes are shown (n = 8–9 mice from two independent experiments). Black and red lines represent tumor growth of mice treated with control and cGAMP (A) or combination (B) therapy, respectively. The number of cured mice is shown under the graph. (C) Gene expression levels in tumor tissues at 6 h after intratumoral treatment with anti-CD47 mAb and/or cGAMP (n = 3; data are representative of two independent experiments). (D–I) After 24 h of the intratumoral treatment, TDLNs were collected and assessed for the total numbers of CD4+, CD8+, CD4+CD69+, and CD8+CD69+ T cells in treated TDLNs (D and E) and untreated TDLNs (F and G; n = 7 mice from two independent experiments). The collected TDLN cells were cocultured with B16F10 or E0771 cells for 24 h. Production of IFN-γ from treated (left, H) and untreated (right, I) TDLN cells was assessed by ELISA (n = 3; data are representative of two independent experiments). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; one-way (C, H, and I) ANOVA with interaction followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test and unpaired t test (D–G).