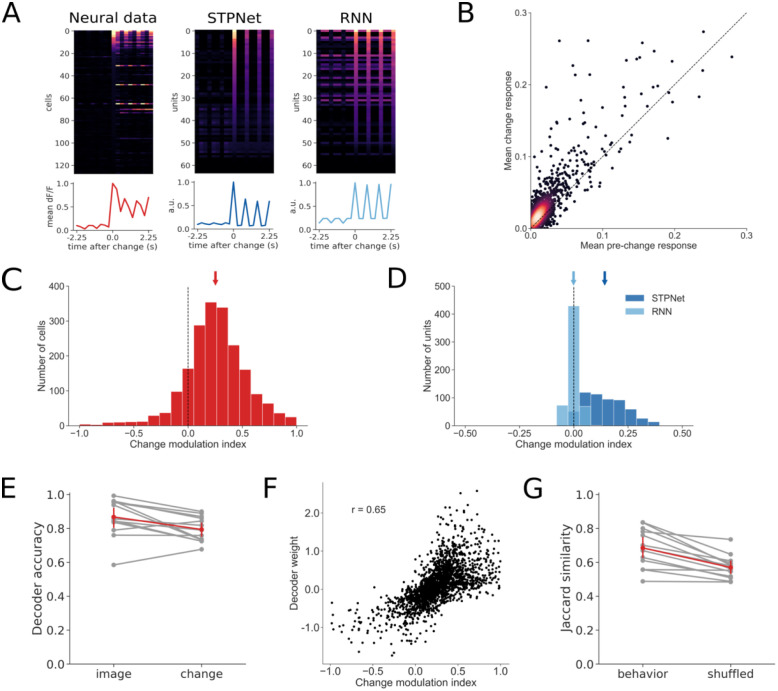
Fig 4. Quantification of change modulation in the experiments and the models.
(A) Example responses centered around the change image time, for the experiments and the two models. The change image was chosen to be the preferred image for either the cell or the model unit under study. The line plots below show the population average time course. (B) A scatter plot of the mean dF/F response on change images versus the mean dF/F response on pre-change images for all neurons recorded in the experiments. Points above the unity line indicate larger mean response on change images versus pre-change images. (C) Quantification of the change modulation index (defined in Methods) in the experiment for the cells shown in panel (B). The mean change modulation index for all cells is positive (mean = 0.25, sem = 0.01) and significantly different than zero (p < 0.001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). (D) Quantification of the change modulation index for units in the first layer of the two models. The STPNet model shows a positive mean change modulation index (mean = 0.14, sem = 0.004), while the RNN model shows a change modulation index close to zero (mean = 0.0, sem = 0.001). The change modulation index is significantly different than zero for the STPNet model (p < 0.001), but not the RNN model (p = 0.26). (E) Mean three-fold cross-validated decoding accuracy for image identity and image change across sessions (N = 13). Both image identity and image change were decodable above chance from population activity. Chance accuracy is 12.5% for image identity and 50% for image change. (F) Scatter plot of average decoder weights and change modulation indices for the neurons recorded in the experiments. A strong positive correlation (r = 0.65) is evident, suggesting that neurons which adapt are informative for change detection. (G) Jaccard similarity between decoder predictions and actual mouse behavior. The decoder predicts mouse behavior better than chance level, as determined by a shuffle control.