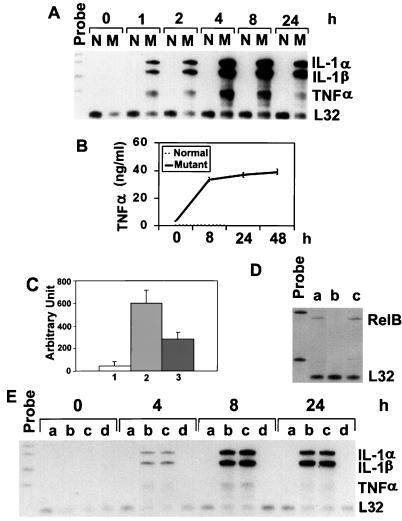
FIG. 1.
Expression of proinflammatory cytokines in normal and relb−/− fibroblasts. (A) IL-1α, IL-1β, and TNF-α mRNA expression in normal (N) and mutant (M) fibroblasts. Total RNA from fibroblasts treated with LPS for the indicated times was analyzed by the RNase protection assay. Riboprobes contain polylinker sequences and are longer than the protected bands. The mouse L32 gene was used as a housekeeping gene. (B) TNF-α protein expression in normal and mutant fibroblasts. Fibroblasts were treated with LPS, and the culture medium was collected at the indicated time points for ELISA analysis. (C) TNF-α promoter activity in fibroblasts as determined by the luciferase assay. Normal and relb−/− fibroblasts were transfected with TNF-α promoter-luciferase plasmids, and the transfected cells were treated with LPS for 12 h and then assayed for luciferase activities (arbitrary units), as described in Materials and Methods. The results are from three independent experiments (means ± standard deviations). Columns 1 and 2, normal and relb−/− fibroblasts transfected with TNFα promoter-luciferase plasmid; column 3, relb−/− fibroblasts transfected with a mutant TNF-α promoter-luciferase plasmid. (D) RelB cDNA-transfection of relb−/− fibroblasts. The expression vector pcDNA, containing a RelB cDNA, was used to transfect relb−/− fibroblasts. Total RNA from positive clones was analyzed for RelB mRNA expression (a). relb−/− fibroblasts transfected with pcDNA vector only (b) and normal fibroblasts (c) were used as controls. (E) Reversal of LPS-induced cytokine overexpression in relb−/− fibroblasts by RelB cDNA transfection. Normal fibroblasts (a), relb−/− fibroblasts (b), relb−/− fibroblasts transfected with pcDNA plasmid (c), and relb−/− fibroblasts transfected with pcDNA vector containing a mouse RelB cDNA fragment (d) were treated with LPS for the indicated times and then analyzed for cytokine expression by the RNase protection assay.