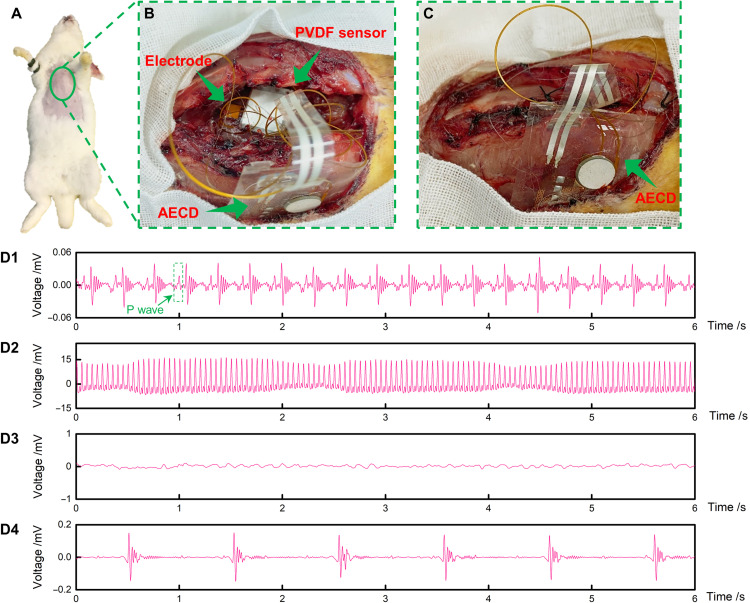
Fig. 5. Cardiac pacing experiment to prove the AECD ability to serve as a cardiac pacemaker.
(A) Experimental animal. (B) Fixing the AECD, sensors, and electrodes. The top arrow shows the PVDF, the middle arrow shows the electrode, and the bottom arrow shows the AECD. (C) Suturing the rabbit’s chest. (D1) Rabbit’s regular heartbeat using ultrasound to power the AECD. (D2) Rabbit ECG, when using a high-voltage AC directly to stimulate the heart to cause cardiac arrest. (D3) Rabbit ECG to confirm that cardiac arrest was initiated successfully. (D4) Rabbit ECG shows that the AECD, powered by ultrasound, successfully detected abnormal heartbeats and stimulated the heart. Photo credit: Peng Jin, Tsinghua University.