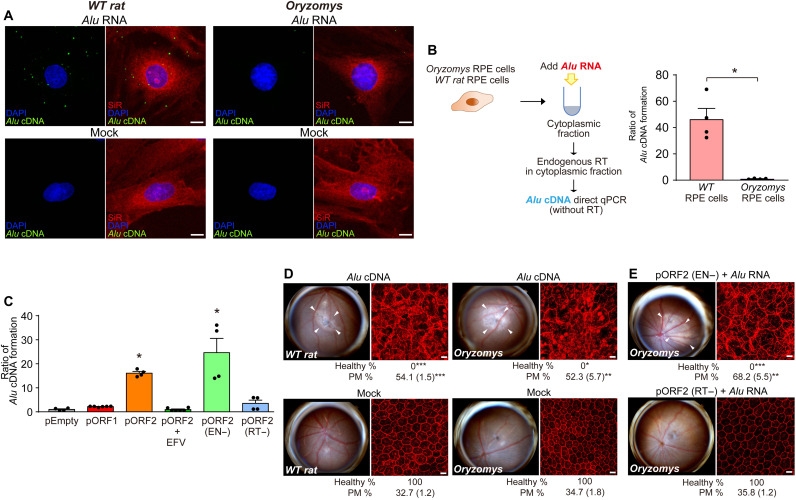
Fig. 4. Cytoplasmic Alu cDNA is synthesized via retrotransposition-independent RT.
(A) Alu cDNA formation monitored by in situ hybridization of RPE cells of R. norvegicus (WT rat) and O. palustris (Oryzomys) transfected with Alu RNA. Green, Alu cDNA; red, SiR-actin; blue, DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. Representative of n = 6. (B) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) of Alu cDNA generated by endogenous RT activity in cytoplasmic fractions of RPE cells of WT rat and O. palustris incubated with Alu RNA. *P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Quantification of Alu cDNA products in cytoplasmic fractions of O. palustris RPE cells by Alu-specific PCR as described above. Cells were transfected with a control plasmid (pEmpty) or plasmids to enforce expression of rat L1 ORF1p, ORF2p (in the presence or absence of EFV), EN-deficient (EN−) ORF2p, or RT-deficient (RT−) ORF2p. *P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. The error bars in (B) and (C) represent the means ± SEM. (D and E) Fundus photographs (left) and corresponding representative RPE sheet micrographs stained for ZO-1 (red) (right) of WT rat and O. palustris. Scale bars, 10 μm. Arrowheads in fundus images denote the boundaries of RPE hypopigmentation. Binary and morphometric quantification of RPE degeneration are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test for binary; two-tailed t test for morphometry. PM, polymegethism [mean (SEM)]. n = 6 to 12. (D) RPE morphology in WT rats and Oryzomys after administration of Alu cDNA or mock injection. (E) RPE morphology in Oryzomys after Alu RNA administration following enforced expression of EN- or RT-deficient L1 ORF2p.