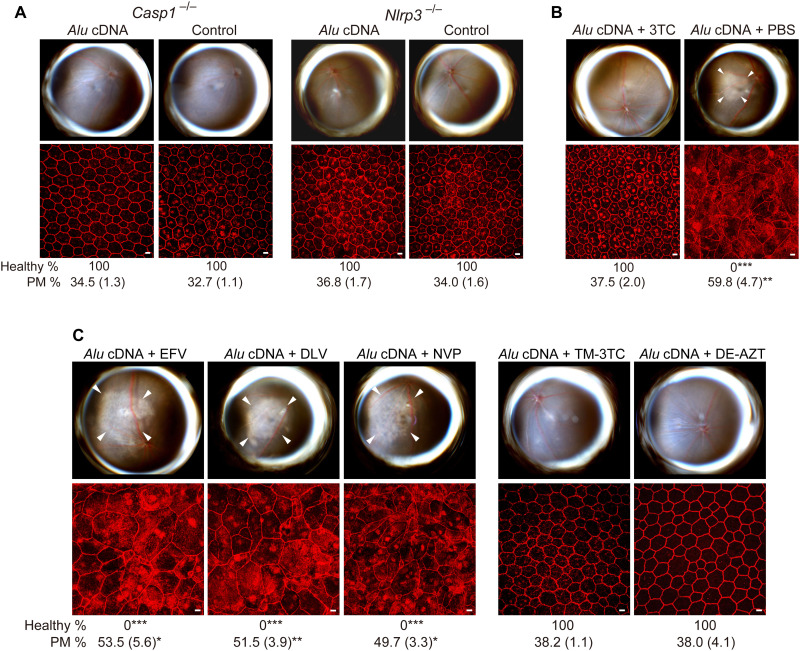
Fig. 9. Alu cDNA induces RPE degeneration via inflammasome activation.
(A to C) Fundus photos (top) and ZO-1–stained (red) RPE flat mounts (bottom) of mice. White arrowheads indicate degenerated area in the fundus images. Scale bars, 10 μm. Binary and morphometric quantification of RPE degeneration are shown (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test for binary; two-tailed t test for morphometry). PM, polymegethism [mean (SEM)]. Arrowheads in fundus images denote the boundaries of RPE hypopigmentation. (A) Casp1−/− (Casp1−/− Casp4129mt/129mt Casp4Tg mice) or Nlrp3−/− mice injected with Alu cDNA or control. n = 6. (B) Effect of 500 pmol of 3TC on Alu cDNA–induced RPE degeneration in WT mice. n = 6. (C) Effect of high doses (500 pmol) of EFV, DLV, or NVP and of trimethyl-3TC (TM-3TC) or diethyl-AZT (DE-AZT) on RPE degeneration in WT mice. n = 4 to 6.