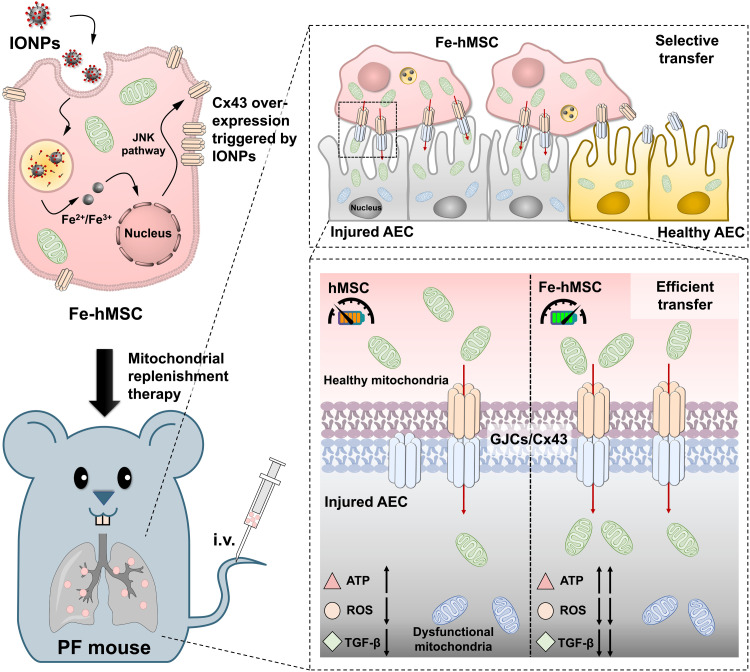
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration showing a potential strategy of using IONPs to augment the intercellular mitochondrial transfer from hMSCs specialized to injured AECs to prevent the progression of PF.
The cellular uptake of IONPs efficiently triggered the up-regulation of Cx43-containing GJCs of hMSCs, probably through c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway activation. These IONP-activated hMSCs (Fe-hMSCs) demonstrated the ability of transferring their healthy mitochondria to injured AECs selectively with a high transfer rate through the Cx43-containing GJCs, bringing significantly improved therapeutic outcomes in recovering adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and decreasing intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and transforming growth factor–β (TGF-β) expression of injured AECs. Consequently, Fe-hMSCs could serve as a living battery of mitochondria to restore the bioenergetics in injured AECs for efficient PF intervention. i.v., intravenous injection.