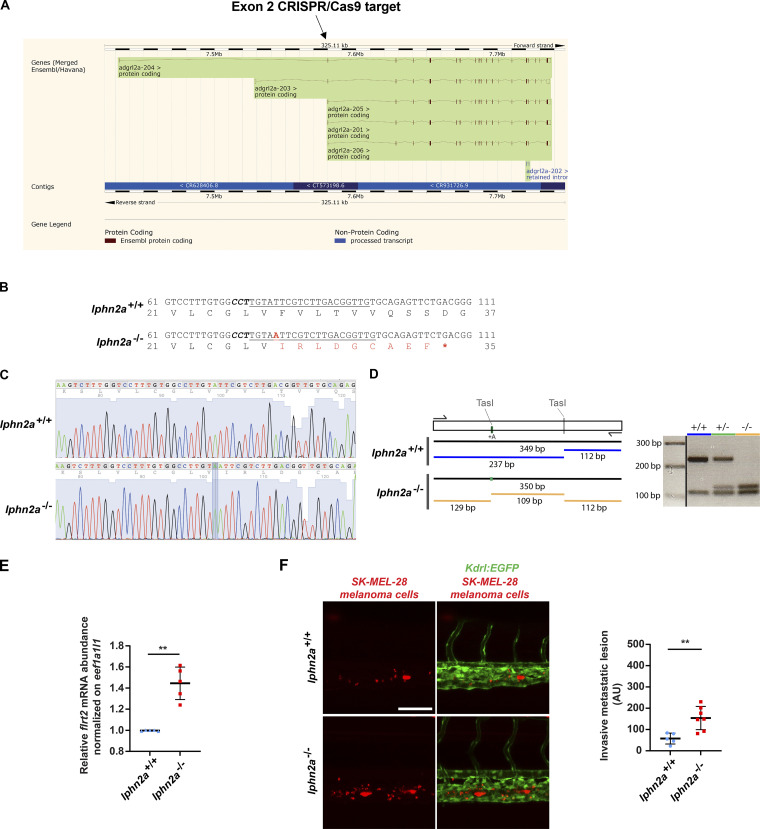
Figure S3.
Generation and characterization of lphn2a null zebrafish embryos. (A) lphn2a (aka adgrl2a) zebrafish mRNA splicing variants displaying all exons. The black arrow outlines the lphn2a gene targeted region located in the second exon, which is common to all splicing variants. (B) DNA sequence details of the exon 2 lphn2a gene targeted region in lphn2a+/+ and lphn2a−/− zebrafish embryos. Locus-specific sgRNA is underlined, and the protospacer-adjacent motif sequence is labeled in bold italics. A one-nucleotide insertion (A, red bold underscored), revealed by sequencing, and the consequent nine new amino acids (red) and STOP codon (red asterisk) are shown. (C) Alignment of lphn2a+/+ and lphn2a−/− sequence obtained by Sanger sequencing. (D) Schematic representation of genotyping. The one base insertion generates a second TasI restriction site in the diagnostic PCR, which has been used for genotyping. (E) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of flrt2 mRNA in lphn2a+/+ or lphn2a−/− zebrafish embryos relative to the housekeeping gene eef1a1l1 and normalized on the mRNA levels measured in lphn2a+/+ animals. Results are the mean ± SD of five independent assays (n > 80 embryos for condition). Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney test; **, P ≤ 0.01. (F) MemBright-560-labeled melanoma cells were microinjected into the duct of Cuvier of 48 hpf lphn2a+/+ or lphn2a−/− Tg(Kdrl:EGFP) zebrafish embryos. After 36 h, extravasated metastatic melanoma cells were imaged by confocal analysis of the caudal plexus. Human SK-MEL-28 melanoma cell extravasation is enhanced in lphn2a−/− compared with lphn2a+/+ zebrafish embryos. Results are the mean ± SD of two independent assays, in which 12 SK-MEL-28 melanoma cell–injected animals were analyzed. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney test; **, P ≤ 0.01.