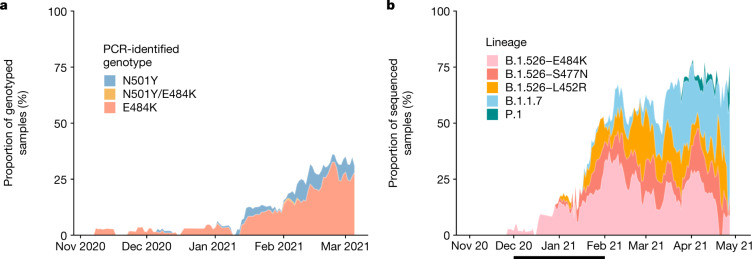
Fig. 1. Prevalence of E484K-harbouring SARS-CoV-2 and B.1.526.
a, Detection of viruses with key signature mutations in spike protein over time. The earliest detected variant with the E484K mutation was collected in mid-November 2020. The prevalence of E484K (samples with E484K/total PCR-genotyped samples) subsequently increased over time, from 1.8% between 1 and 15 December 2020 to 26.1% between 1 and 15 March 2021. Throughout late 2020 and early 2021, we identified fewer isolates with N501Y than with E484K, with a maximum of 5.9% of isolates containing N501Y in mid-February 2021. b, Distribution of different viral lineages identified by whole-genome sequencing. Within our collection of SARS-CoV-2 genomes (n = 1,507), the B.1.526 lineage rapidly increased in prevalence in early 2021, replacing the majority of other lineages (the blank space) present during this timeframe. This was followed by a steady rise in B.1.1.7 by mid-2021. The line below the x axis denotes the time period used to calculate the growth advantage of B.1.526 over other viruses that appeared earlier.