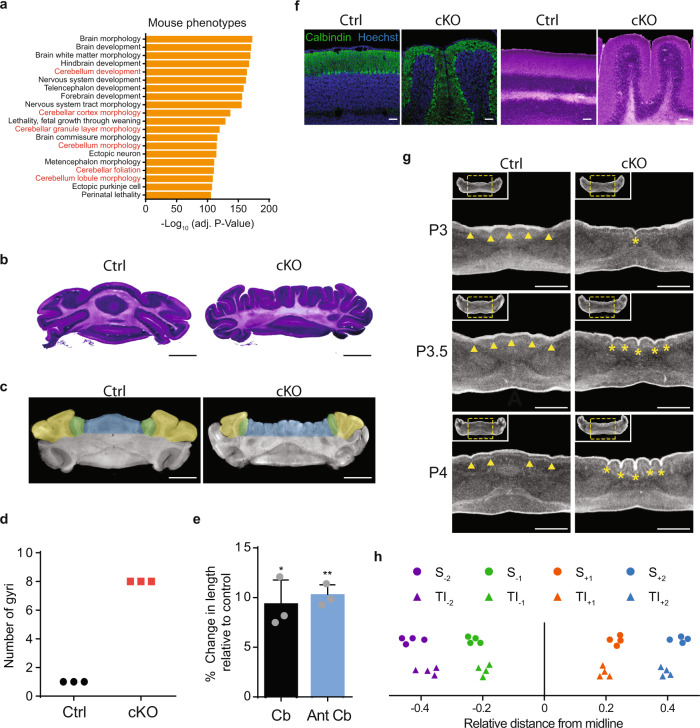
Fig. 4. Conditional knockout of CHD7 results in stereotyped cerebellar microgyria.
a GREAT analysis showing enriched mouse phenotypes associated with CHD7-regulated genes. Cerebellar phenotypes shown in red text. b Hematoxylin and eosin staining of Ctrl (left) and CHD7 cKO (right) p56 sections of mouse cerebellum. Scale bar: 2 mm. c Zeiss Xradia Versa 520 XRM was used to perform a nano-computerized tomography (nano CT) scan of Ctrl (left) and cKO (right) p56 mouse cerebella. The cerebellar vermis is highlighted blue and corresponding hemisphere regions highlighted green and yellow. Scale bar: 2 mm. d Graph showing number of gyri in the cerebellar vermis of the anterior basal lobe of Ctrl and cKO mice (n = 3 for each condition). e Bar graphs showing % change in total cerebellar (Cb) and anterior lobules (Ant Cb) lengths upon CHD7 cKO (n = 3 for each condition). Length is shown as mean ± s.e.m for each measurement. p = 0.0188 (Cb), p = 0.0024 (Ant Cb) Paired two-sided t-test. f IHC (left) and H&E (right) of Ctrl and cKO p56 mouse cerebellar sections. Experiment was repeated three times for each condition. Scale bars: 100 µm. g Nano CT scans were taken of P3, P3.5, and P4 mice cerebella. Digital 2D sections were taken through anterior basal lobe lobules. Insets show entire cerebellar section. Yellow dashed squares define region of focus. Yellow arrowheads on P4 Ctrl section mark transient vermal indentations. Yellow asterisks on P4 cKO section mark aberrant sulci. Scale bars: 500 µm. h Dot plot showing relative distance of transient invaginations (TI) in P4 CHD7 ctrl mice (n = 4) and sulci (S) formation in P4 CHD7 cKO mice (n = 4).