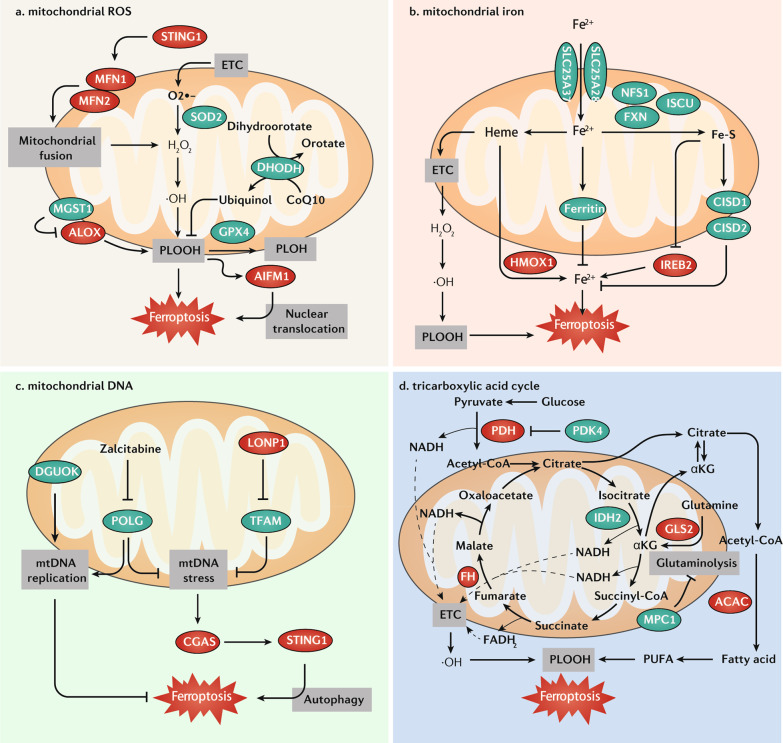
Fig. 2. Role of mitochondria in ferroptosis.
a Mitochondrial ROS. GPX4, SOD2, and MGST1 are mitochondria-associated antioxidant proteins, which play a major role in protecting mitochondria from oxidative damage during ferroptosis. In addition, mitochondrial DHODH limits ferroptosis through the reduction of CoQ10 to ubiquinol. Mitochondrial oxidative damage induces the release of AIFM1, which promotes ferroptosis through its translocation to the nucleus. The STING1-MFN1/2 pathway triggers ferroptosis by inducing mitochondrial fusion and subsequent ROS production. b Mitochondrial iron. Iron can be transported to the mitochondria via SLC25A37 and SLC25A28 and used to synthesize heme/Fe-S, or it can be stored in ferritin in mitochondria. Heme is catalyzed by HMOX1 and decomposes into Fe2+, and acts as a key cofactor of ETC by which heme promotes ferroptosis. The inhibition of iron-sulfur cluster assembly proteins, including NFS1, FXN, and ISCU, can enhance ferroptosis by the activation of an IREB2-mediated iron-starvation response. Fe-S proteins CISD1 and CISD2 inhibit ferroptosis by decreasing intracellular iron levels. c Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). POLG (DNA polymerase) and DGUOK (deoxynucleoside synthesis enzyme) are required for mtDNA replication. The inhibition of POLG by zalcitabine and TFAM degradation induce mtDNA stress, which activates GAS-STING1 pathway-dependent autophagy to mediate ferroptosis. d The TCA cycle transfers electrons to the ETC, which releases ROS to induce ferroptosis. The TCA cycle also enhances ferroptosis by promoting ACAC-mediated fatty acid synthesis. This effect is inhibited by PDK4-mediated glucose metabolism or enhanced by GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis. In addition, the suppression of MPC1 also enhances ferroptosis partly through increasing glutaminolysis. Abbreviations: ACAC acetyl-CoA carboxylase, AIFM1/AIF apoptosis-inducing factor mitochondria-associated 1, ALOX lipoxygenase, CGAS cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, CISD1 CDGSH iron sulfur domain 1, CISD2 CDGSH iron sulfur domain 2, DGUOK deoxyguanosine kinase, DHODH dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), ETC electron transport chain, FH fumarate hydratase, FXN frataxin, GLS2 glutaminase 2, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, HMOX1/HO1 heme oxygenase 1, IDH2 isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP[+]) 2, IREB2/IRP2 iron-responsive element binding protein 2, ISCU iron–sulfur cluster assembly enzyme, LONP1 Lon peptidase 1, mitochondrial, MFN1 mitofusin 1, MFN2 mitofusin 2, MGST1 microsomal glutathione S-transferase 1, MPC1 mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1, NADH dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase, PDK4 pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4, PLOOH phospholipid hydroperoxide, POLG DNA polymerase gamma, catalytic subunit, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acid, ROS reactive oxygen species, SLC25A28/mitoferrin-2 solute carrier family 25 member 28, SLC25A37/mitoferrin-1 solute carrier family 25 member 37, SOD2 superoxide dismutase 2, STING1/TMEM173 stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor 1, TFAM transcription factor A, mitochondrial.