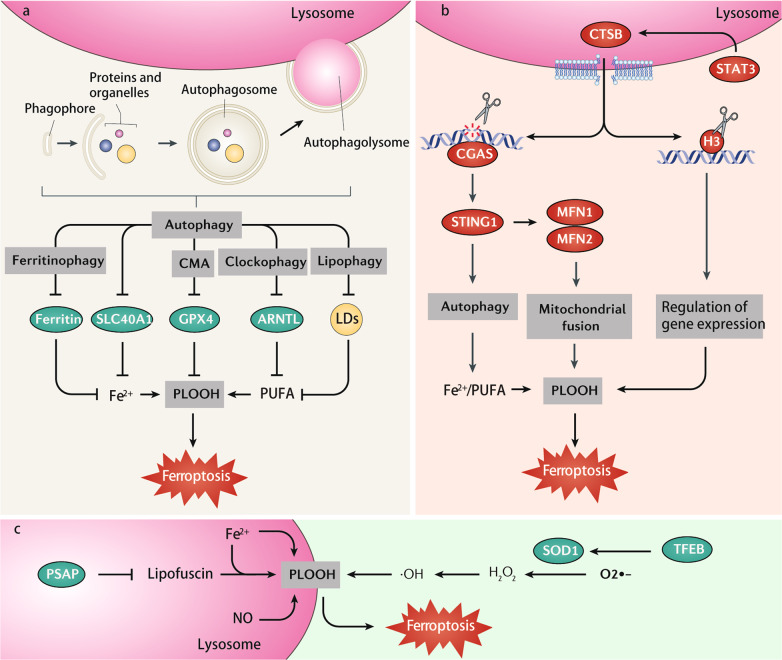
Fig. 3. Role of lysosomes in ferroptosis.
a Several selective autophagy pathways (ferritinophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy [CMA], clockophagy, and lipophagy) promote ferroptosis by removing different cargoes, including ferritin, SLC40A1, GPX4, ARNTL, and lipid droplets (LDs). b Lysosomal CTSB is considered as an executioner of ferroptosis. CTSB is upregulated by the activation of transcription factor STAT3. CTSB translocates from lysosomes to the nucleus, where it cleaves DNA or histone H3. CTSB-mediated DNA damage activates STING1-dependent autophagy, while H3 cleavage might change ferroptosis-related gene expression. c The accumulation of lysosomal iron or nitric oxide (NO) can promote lysosome-dependent ferroptosis through induction of lipid peroxidation. The inhibition of PSAP triggers an accumulation of lipofuscin, which traps iron to induce ferroptosis. TFEB-mediated SOD2 expression attenuates ferroptosis by inhibiting ROS production. Abbreviations: ARNTL/BMAL1 aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like, CGAS cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, CTSB cathepsin B, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, H3 histone H3, MFN1 mitofusin 1, MFN2 mitofusin 2, PLOOH phospholipid hydroperoxides, PSAP prosaposin, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acid, SLC40A1 solute carrier family 40 member 1, SOD1 superoxide dismutase 1, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, STING1/TMEM173 stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor 1, TFEB transcription factor EB.