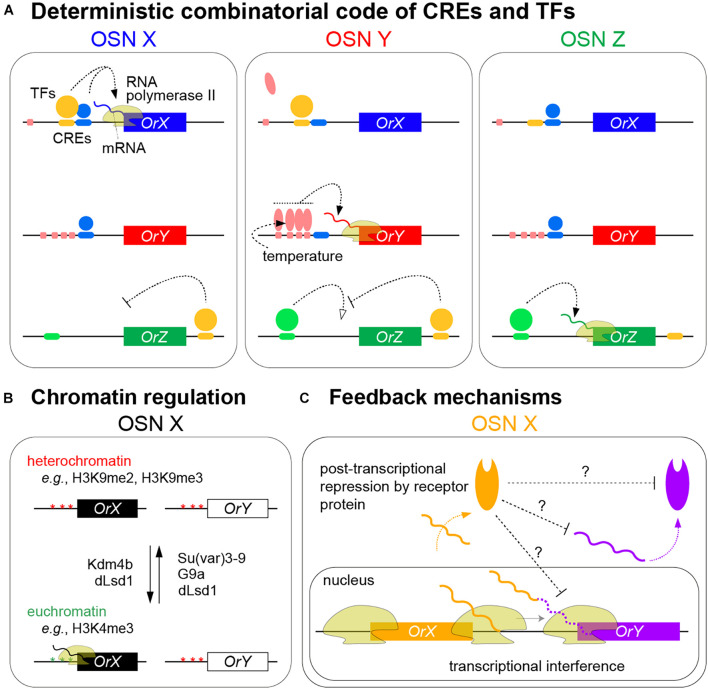
FIGURE 2.
Models of olfactory receptor expression in insects. (A) Summary of the mechanisms ensuring the neuron-specific transcription of olfactory receptors through the combinatorial action of CREs and TFs to promote RNA polymerase II transcription of a specific receptor gene in an olfactory sensory neuron (OSN) (only the neuronal nuclei are shown). In these hypothetical examples, OrX requires binding of both yellow and blue TFs to corresponding CREs to be expressed; either alone is insufficient. OrY requires the cooperative binding of the red TF to clustered CREs for expression; this cooperation can ensure robust expression in the face of environmental temperature changes; by contrast, the red TF does not bind to the single corresponding CRE upstream of OrX in these neurons. OrZ transcription is promoted by the green TF but suppressed by the yellow TF that binds 3′ of the gene. Other external factors might influence levels, though not spatial patterning, of receptor expression (see text). (B) Chromatin marks and histone-modifying enzymes contributing to the selective expression of olfactory receptors. Different enzymes display differences in their temporal expression and requirement; among these, dLsd1 – which is normally associated with removing H3K4 methylation – appears to have roles in OSNs in both promoting and repressing Or expression (see text). Although schematized separately for clarity, chromatin regulation is intimately related to the combinatorial binding of TFs to receptor loci. (C) Feedback mechanisms contributing to the refinement and/or stability of receptor expression. Transcriptional interference by OrX of OrY might occur when inefficient transcriptional termination at the 3′ end of the former gene leads to the RNA polymerase II impeding transcription initiation at OrY (solid wavy orange and purple lines represent protein coding transcripts from OrX and OrY, respectively; the dashed purple line represents the 3′UTR of OrX transcripts that incorporate sequences encoded by OrY that are not translated into OrY) (Mika et al., 2021). Receptor protein-dependent feedback on transcript or protein levels of other (not necessarily closely linked) receptors occurs through unknown mechanisms (Maguire et al., 2020; Jafari et al., 2021; Mika et al., 2021).