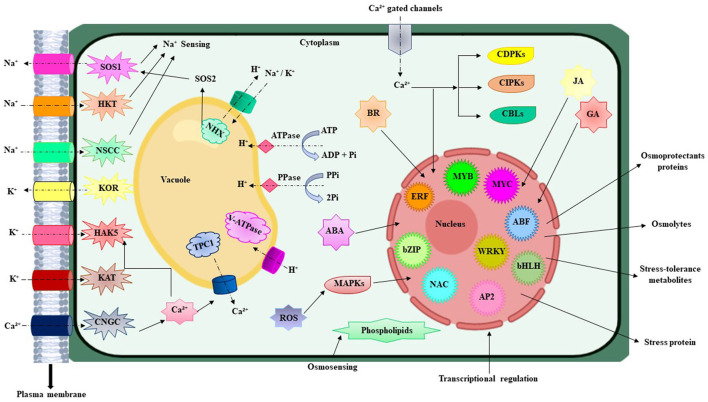
Figure 2.
Illustrated the simplified overview of different component for salt response and salt tolerance mechanism in plants. Na+ cross the plasma membrane through CNGC, HKT, NSCCs, and some other unknown gated channels (showed as dotted black arrows). This ion imbalance causes the modification in membrane voltage flux and disturbs the inflow and outflow of Ca2+ and K+ ion. After the Na+ import into the cell, different unidentified ionic and hyperosmotic sensory networks initiate the early sensing. This resulted in the activation of certain Ca2+ gate channels and triggered the detoxification pathways via HKT, KOR, KAT, HAKS, and antiporter SOS1 and maintains the ion balance within the cell. SOS1 moves out the Na+ from the root cortex while HKTI allows the reverse flux and discharge Na+ from xylem to stop the hyperaccumulation in photosynthetic cells. The ionic stress is also tackled via sequestration by means of NHX channels that import the K+ or Na+ and moves out the H+ from the vacuole. H+ ions are also transported by the V-ATPase, PPase, and ATPase in opposite direction. Ca2+ export from the vacuole through TPC1 and helps to maintain the ionic and osmotic balance. At the next step, Ca2+ produces ROS that showed a positive correlation between them. This activated the signaling pathways of CDPKs, CIPKs, and CBLs which after entry imitates the transcriptional modification. The expression of several gene families is controlled at transcriptional level including MYB, MYC, ERF, bZIP, NAC, WRKY, ABF, AP2, and bHLH change which ultimately provide salt stress tolerance to plants. Also, ABA-mediated pathways triggered the production of JA, BR, and GA that helps the plant to recover from the salinity syndrome. NSCCs, non-selective cation channels; SOS, salt overly sensitive; HKT, high-affinity potassium transporter; KOR, potassium outward-rectifying; HAKs, high-affinity K+ transporters; CNGC, cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel; NHX, sodium hydrogen exchanger; TPC1, two-pore Channel 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MAPKS, mitogen activated protein kinases; CIPKs, CBL-interacting protein kinases; CBLs, calcineurin Blike proteins; CDPKs, calcium-dependent protein kinases; bZIP, basic leucine zipper; AP2/ERF, Apetala2/ethylene response factor; JA, jasmonic acid; BR, Brassinosteroids; GA, Gibberellic acid. Signs: Ion transport (dotted arrow), promotion (arrow).