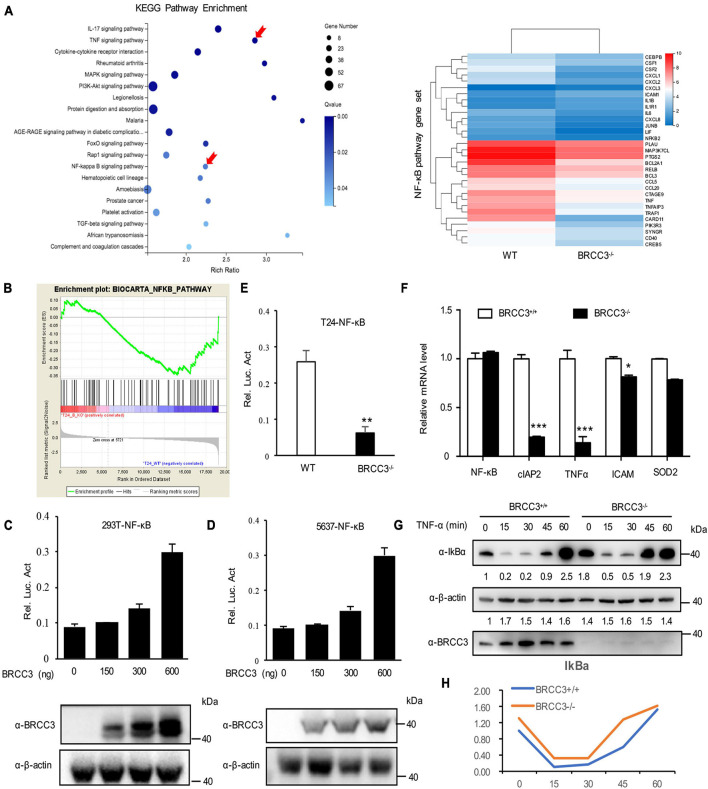
FIGURE 4.
Knocking out of BRCC3 resulted in inactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was used to assess wild type and BRCC3–/– bladder cancer cells. (B) GSEA identified NF-κB pathway-related gene sets enriched in the wild-type cells. (C) BRCC3 promotes the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. 293T cells were transfected with an NF-κB reporter firefly luciferase plasmid (200 ng), pRL-TK (10 ng) and the indicated amounts of a BRCC3 plasmid. Reporter assays were performed 48 h after transfection, and the results are presented as the NF-κB/TK luciferase activity. Data were analyzed employing one-way ANOVA and presented as the means ± standard error (n = 3/group). (D) BRCC3 promoted the transcriptional activity of NF-κB in bladder cancer 5637 bladder cancer cells. The experiments and data analyses were performed as in (C). (E) BRCC3 ablation inhibited the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. (F) The BRCC3 deficiency blocked the transcription of NF-κB-targeted genes in the T24 cells. The expression levels of the indicated NF-κB-targeted genes were examined by RT-qPCR in BRCC3–/– T24 cells and wild type T24 cells. (G) BRCC3 deficiency reduced the degradation of IκBα under TNFα stimulation. BRCC3–/– T24 cells and wild type T24 cells were treated with 5 ng/ml TNFα for indicated time, and then the cell total protein lysis was analyzed by immunoblotting assays. (H) Quantitative data show the relative protein levels of IκBα in (G). Statistical analysis was conducted using a t-test. The means ± standard error from three independent experiments is shown. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.001, and ***P< 0.001 compared with controls.