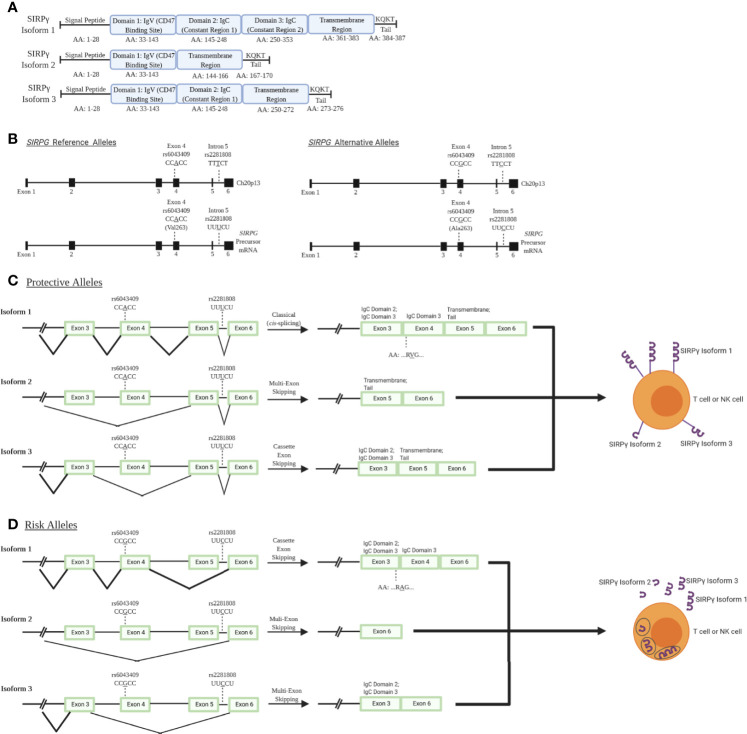
Figure 1.
SIRPγ isoforms and predicted consequences of rs2281808 and rs6043409 SNPs: T1D-associated SNPs in signal regulatory protein gamma (SIRPG) may alter splicing activity and thereby surface SIRPG expression. (A) Isoform 1 (NCBI Reference Sequence: NP_061026.2) is the longest and most predominant form of the protein, while isoform 2 (NP_543006.2) and isoform 3 (NP_001034597.1) are shorter and less frequently observed (18, 19). All isoforms contain domain 1 (D1), which is the immunoglobulin variable (IgV) region that binds to CD47. However, only isoform 1 contains two immunoglobulin constant (IgC) regions and a known transmembrane region at the end of the protein structure. Isoform 3 contains at least one IgC, while isoform 2 has no constant region. (B) Gene and pre-mRNA diagrams of SIRPG (NCBI reference sequence for gene: NC_000020.11, Gene ID: 55423; precursor mRNA for isoform 1: NM_018556.41). Reference and alternative alleles for rs2281808 and rs6043409 are shown. (C) We speculate that the protective alleles of rs2281808 and rs6043409 are associated with “normal” SIRPG splicing and high membrane SIRPγ expression on T cells and NK cells, while (D) SIRPG risk alleles might promote aberrant splicing, potentially resulting in a loss of exon 5, which encodes most of the transmembrane region. We expect this would cause lower membrane expression of SIRPγ as well as increased SIRPγ secretion.