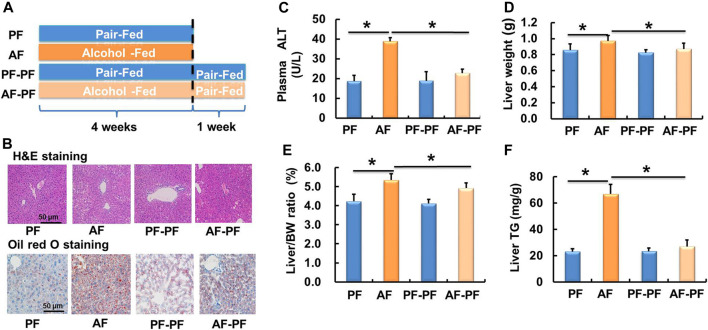
FIGURE 1.
Alcohol withdrawal ameliorates alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and liver injury. (A) Schematic diagram of the research design. (B) H & E staining and oil red O staining photomicrographs of the liver section (magnification, 100x). (C) Plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level. (D) Live weight. (E) Liver weight/body weight ratio. (F) Triglyceride (TG) content in the liver. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences (n = 8).