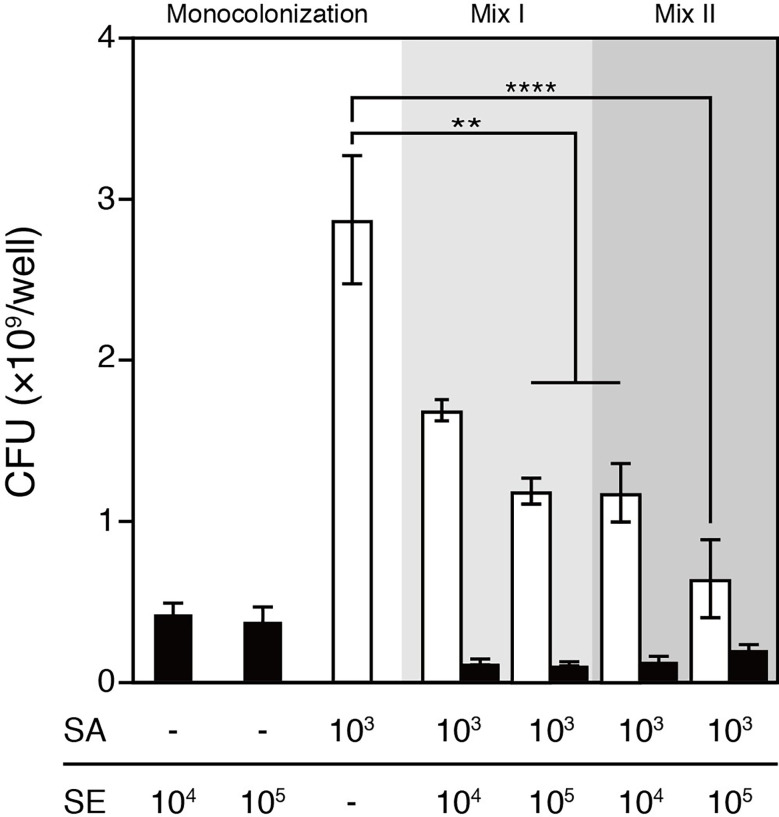
Figure 2.
Viable counts of S. aureus and/or S. epidermidis that colonized the surface of the 3D epidermal model after 48h cultivation. The viable counts of S. aureus were significantly lower in the coculture with S epidermidis than in S. aureus monoculture. Increasing the infective dose of S. epidermidis from 104 to 105 CFU/well or inoculating S. epidermidis 4h prior to S. aureus further reduced the viable counts of S. aureus that colonized the epidermal surface. SE, S. epidermidis (black bars); SA, S. aureus (open bars); Mix I, S. epidermidis and S. aureus were inoculated simultaneously; Mix II, S. epidermidis was inoculated 4h prior to S. aureus. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3-6). **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001. Tukey–Kramer Post Hoc test after One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).