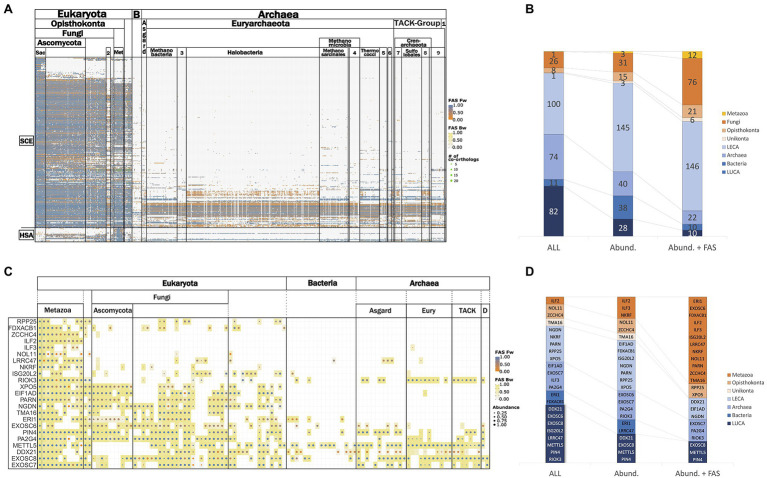
Figure 3.
Representation of RBFeuk orthologs across the three domains of life. (A) Phylogenetic profile of the RBFeuk set summarized on the class-level. Proteins are represented by the rows and columns represent the analyzed taxa. A dot in the matrix indicates that an ortholog for the respective RBF was found in this taxon. The dot color informs about the domain architecture similarity between the detected ortholog and the seed protein. (B) Phylostratigraphy of the RBFeuk set based on the data shown in (A) filtered at varying levels of stringency (see main text). LECA – last eukaryotic common ancestor; Archaea – orthologs to an RBF are present in the archaea but not in the bacteria; Bacteria – orthologs to an RBF are present in bacteria but not in archaea; and last universal common ancestor (LUCA) – an ortholog was present both in archaea and bacteria. The two positive controls are placed in the Archaea stratum for the All and the Abundance filter, but are placed in LECA in the Abund. + FAS filter. (C) Phylogenetic profiles of the RBFhuman set summarized on the class level. The corresponding phylostratigraphies are shown in (D).