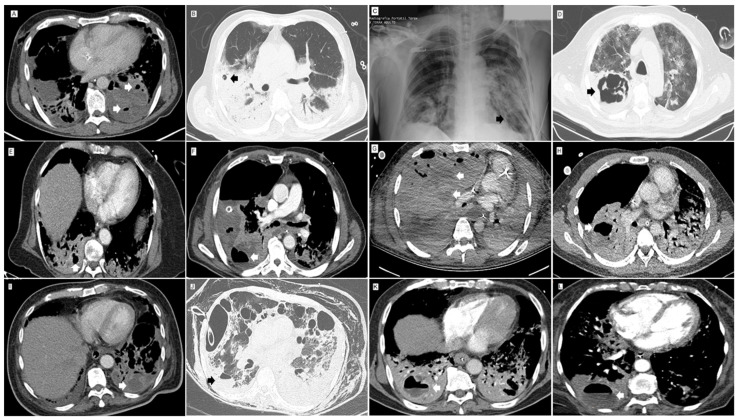
Figure 1.
Lung images of post-COVID-19 necrotizing pneumonia. (A) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Low density area of the left lower lobe lung parenchyma with loss of parenchymal enhancement, with architectural distortion and small abnormal gas-filled spaces (arrows) due to necrotizing pneumonia. (B) Non-contrast CT. Lung Window. Small round 9 mm thin-walled, air-filled lesion (pneumatocele) (arrow) in a right upper lobe area of consolidation. (C) Chest X-Ray. Well-defined 20 mm thin-walled area of parenchymal lucency (arrow) within area of consolidation in the left lower lobe. Pneumothorax. (D) Non-contrast CT. Lung Window. Thick-walled and irregular cavity (arrow) with septum due to lung abscess within area of necrotizing pneumonia. (E) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Heterogeneous attenuation of the right lower lobe lung parenchyma with a consolidation pattern with low-density areas, loss of parenchymal enhancement and small air-filled rounded lesions (arrow) due to necrotizing pneumonia. (F) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Large low-density area with loss of parenchymal enhancement of the right upper lobe lung parenchyma associated with thin-walled air-fluid level cavity due to necrotizing pneumonia with lung abscess. Large air-fluid level (arrow) in the pleural space due to empyema. (G) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Large area with increase in parenchymal attenuation with a consolidation pattern and low-density areas (arrows), loss of parenchymal enhancement, architectural distortion, and peripheral air-filled rounded lesions due to necrotizing pneumonia. (H) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Low-density area with loss of parenchymal enhancement in the right lower lobe, associated with adjacent cavitary lesion (arrow) due to necrotizing pneumonia and lung abscess. (I) Contrast CT. Mediastinal Window. Area of consolidation in the left lower lobe with low-density areas (arrow) of liquid content with subtle peripheral enhancement due to necrotizing pneumonia with abscess. (J) Non-contrast CT. Lung Window. A 3-cm thin-walled collection with air-fluid level (arrow) due to superinfection of a lung cavity or abscess in the right lower lobe. (K) CT pulmonary angiography. Mediastinal window. Bilateral lower lobe consolidation and collection with air-fluid level (arrow) with peripheral enhancement in right lower lobe due to lung abscess. (L) CT pulmonary angiography. Mediastinal window. Collection with air-fluid level (arrow) with low peripheral enhancement in right lower lobe consolidation due to lung abscess.