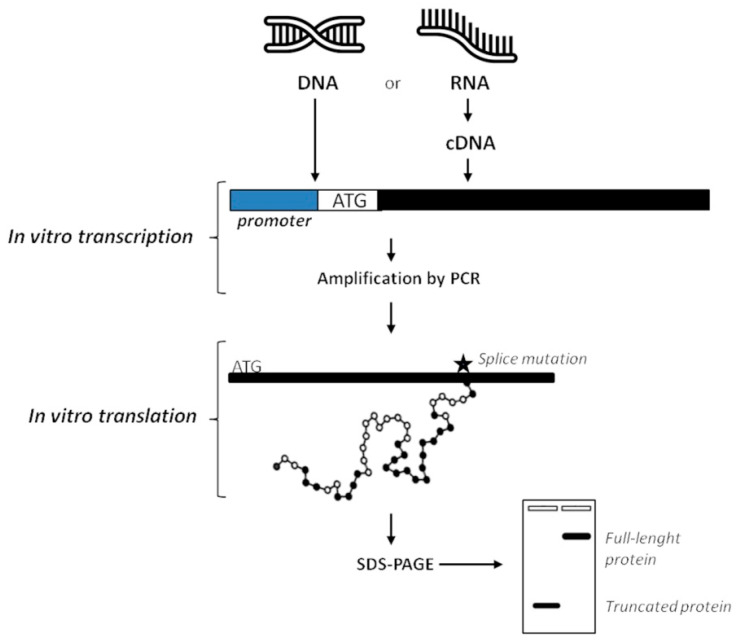
Figure 5.
Overview of the protein truncation test. DNA or cDNA obtained from RNA by retrotrascription can be used as a template to perform PCR. During amplification process, an RNA polymerase promoter and a translation initiation sequence (ATG) are added to products, together with a consensus Kozak sequence to improve the process. Then, the RNA polymerase promoter initiates transcription and the ATG sequence is used to start translation of RNA into protein. PCR fragments are then separated on basis of their size by agarose gel-electrophoresis, and mutations affecting splicing can be revealed. In the radioactive PTT, addition of radiolabelled amino acids in nascent proteins requires blotting after SDS-PAGE and then exposition to X-ray to analyze results (not shown). Finally, only DNA sequencing can confirm if the production of truncated proteins is due to aberrant splicing.