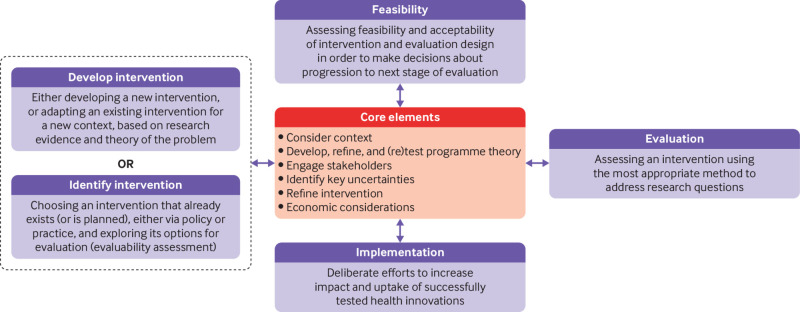
Fig 1.
Framework for developing and evaluating complex interventions. Context=any feature of the circumstances in which an intervention is conceived, developed, evaluated, and implemented; programme theory=describes how an intervention is expected to lead to its effects and under what conditions—the programme theory should be tested and refined at all stages and used to guide the identification of uncertainties and research questions; stakeholders=those who are targeted by the intervention or policy, involved in its development or delivery, or more broadly those whose personal or professional interests are affected (that is, who have a stake in the topic)—this includes patients and members of the public as well as those linked in a professional capacity; uncertainties=identifying the key uncertainties that exist, given what is already known and what the programme theory, research team, and stakeholders identify as being most important to discover—these judgments inform the framing of research questions, which in turn govern the choice of research perspective; refinement=the process of fine tuning or making changes to the intervention once a preliminary version (prototype) has been developed; economic considerations=determining the comparative resource and outcome consequences of the interventions for those people and organisations affected