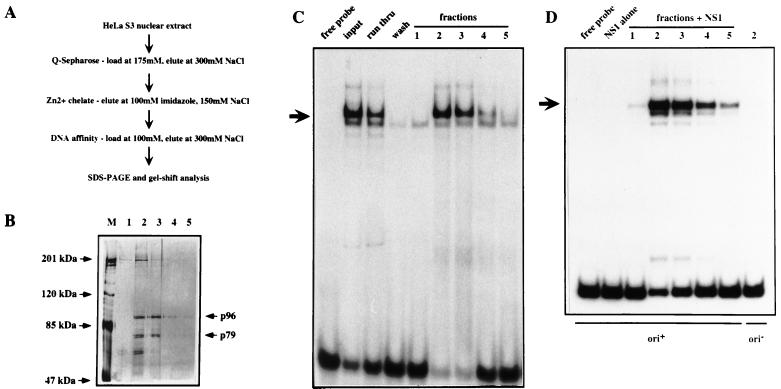
FIG. 2.
Purification and analysis of the HeLa PIF complex. (A) Fractionation scheme used to purify PIF from HeLa nuclear extracts. (B) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing fractions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 eluted from the site-specific DNA affinity chromatography. Lane M contains molecular mass markers. (C) EMSA analysis of fractions. The input is a PIF fraction from a Zn2+-metal chelate Sepharose column which was loaded on to the site-specific DNA affinity column; run thru is the unbound material; wash is the last column wash before elution; lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are serial fractions obtained by elution with 300 mM NaCl. (D) Eluted fractions catalyze nicking and covalent attachment of NS1 to the minimal MVM origin. Nicking assay mixtures contained 100 ng of GST-NS1 and ATP; samples in lanes labeled 1 through 5 also received fractions eluted from the DNA affinity column. The nicking assay in the last lane was performed in the presence of fraction 2, GST-NS1, and ATP but using a control substrate (ori−), in which a single extra nucleotide inserted into the bubble sequence inactivates viral replication origin function (7).