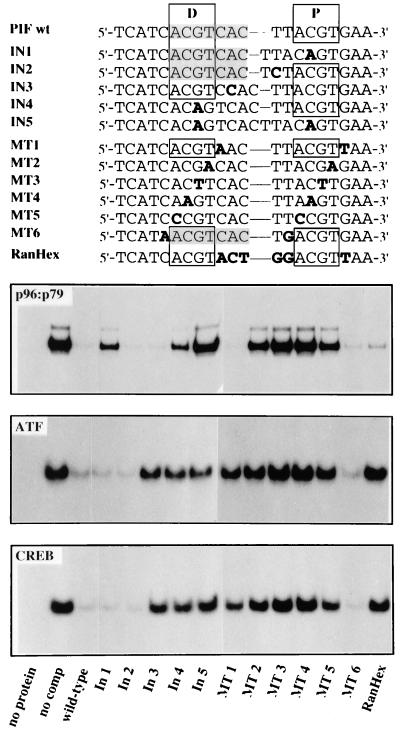
FIG. 5.
Recombinant PIF heterodimers bind spaced, bipartite ACGT motifs. Sequences of double-stranded oligonucleotides, representing wild-type and mutant forms of the PIF-binding region in the MVM 3′ origin that were used as competitors in the EMSAs, are shown at the top. Positions of wild-type proximal (P) and distal (D) ACGT half-sites are boxed, and the ATF/CREB-binding site is shaded. Individually mutated nucleotides are indicated in bold type. The lower three panels compare rPIF-, rATF1-, and rCREB-binding specificities on these sequences by competitive EMSA with 100-fold molar excesses of the wild-type or mutant competitor oligonucleotide. Assay mixtures contained the same 32P-labeled PIF wild-type oligonucleotide probe and constant amounts of rPIF, rATF1, or rCREB, as indicated in each panel.