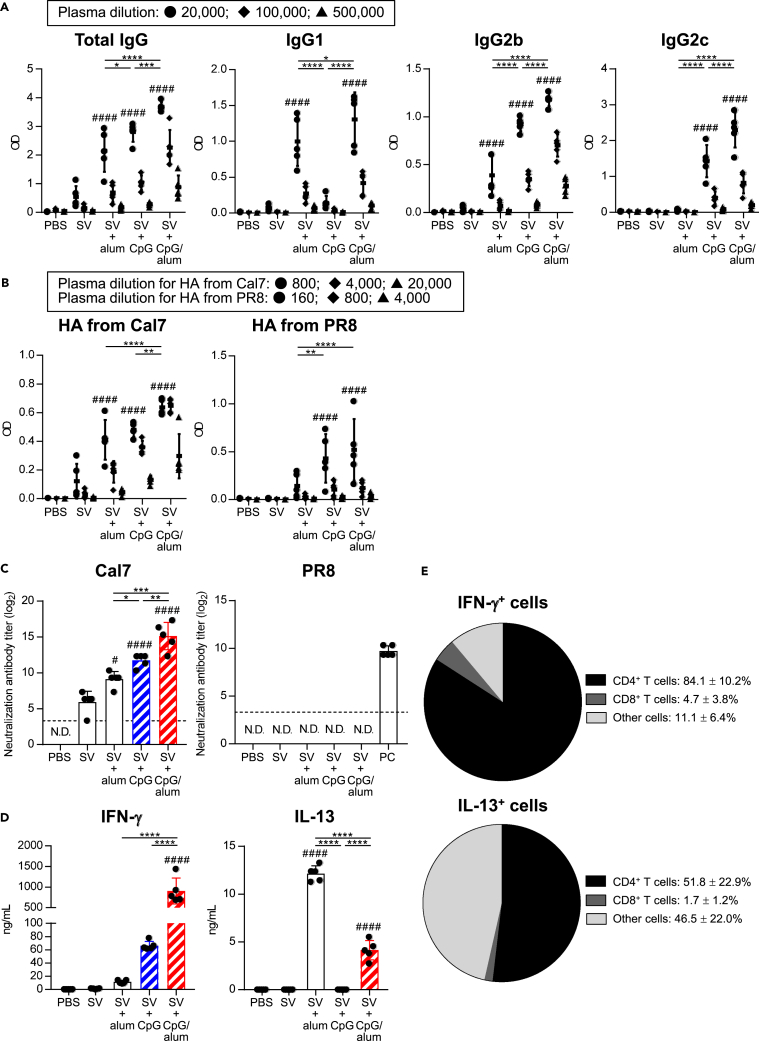
Figure 1.
Antibody responses after the combined use of CpG–ODN and alum as adjuvants
Mice were immunized with SV alone, SV plus alum, SV plus CpG–ODN, or SV plus CpG/alum subcutaneously. As a control, mice were treated with PBS subcutaneously.
(A and B) Levels of (A) SV-specific total mIgG, mIgG1, mIgG2b, and mIgG2c in the plasma, and (B) rHA from Cal7-and rHA from PR8-specific total mIgG in the plasma were determined after final immunization. We used (A) 20,000- (●), 100,000- (◆), and 500,000- (▲) fold–diluted plasma samples,(B) 800- (●), 4,000- (◆), and 20,000- (▲) fold–diluted plasma samples for rHA from Cal7, and 160- (●), 800- (◆), and 4,000- (▲) fold-diluted plasma samples for rHA from PR8.
(C) Neutralization titers against Cal7 and PR8 in the plasma samples from immunized mice were determined using MDCK cells. Plasma samples from PR8-immunized mice were used as a positive control (PC). N.D.: not detected. The dashed line shows the detection threshold for a positive response.
(D) Splenocytes obtained from immunized mice were incubated in the presence of SV in vitro and the levels of IFN-γ and IL-13 in the supernatants were measured after 3 days.
(E) Splenocytes obtained from SV plus CpG/alum-immunized mice were incubated in the presence of SV with the protein transport inhibitor cocktail for 24 h in vitro and the intracellular IFN-γ and IL-13 levels were evaluated by flow cytometry.(A–E) n = 5 per group. Data are means ± SD. #p<0.05, ####p<0.0001 vs. SV alone group; ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01, ∗∗∗p<0.001, ∗∗∗∗p<0.0001 as indicated by Tukey’s test. Significant differences were analyzed only in the (A) 20,000-fold-diluted plasma samples, (B) 800-fold-diluted plasma samples for rHA from Cal7 and 160-fold-diluted plasma samples for rHA from PR8. See also Figures S1 and S2.