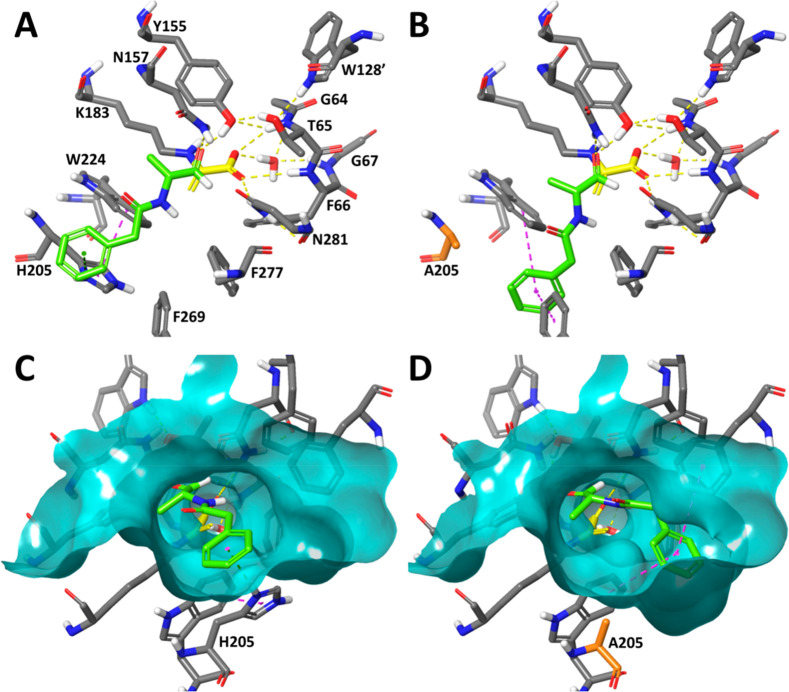
Figure 3.
Models of the prereactive complexes of wild-type HBPA (A, C) and HBPA H205A (B, D) with the covalently bound pyruvate enamine (yellow C atoms) and aldehyde 1o (green C atoms). The mutated residue is highlighted in orange. Interactions are shown with dashed lines: H bonds in yellow, π-stacking in magenta, and π-cation in dark green. A comparison of the surface of the active sites of both proteins (C, D) (transparent cyan) reveals that the H205A mutation generates an expanded cavity near residue A205, which can be occupied by the phenyl moiety of 1o. These models were obtained by QM/MM optimization of the structure of the complexes at the DFT (B3LYP/6-31G**) level of theory, as detailed in the Supporting Information.