Figure 3.
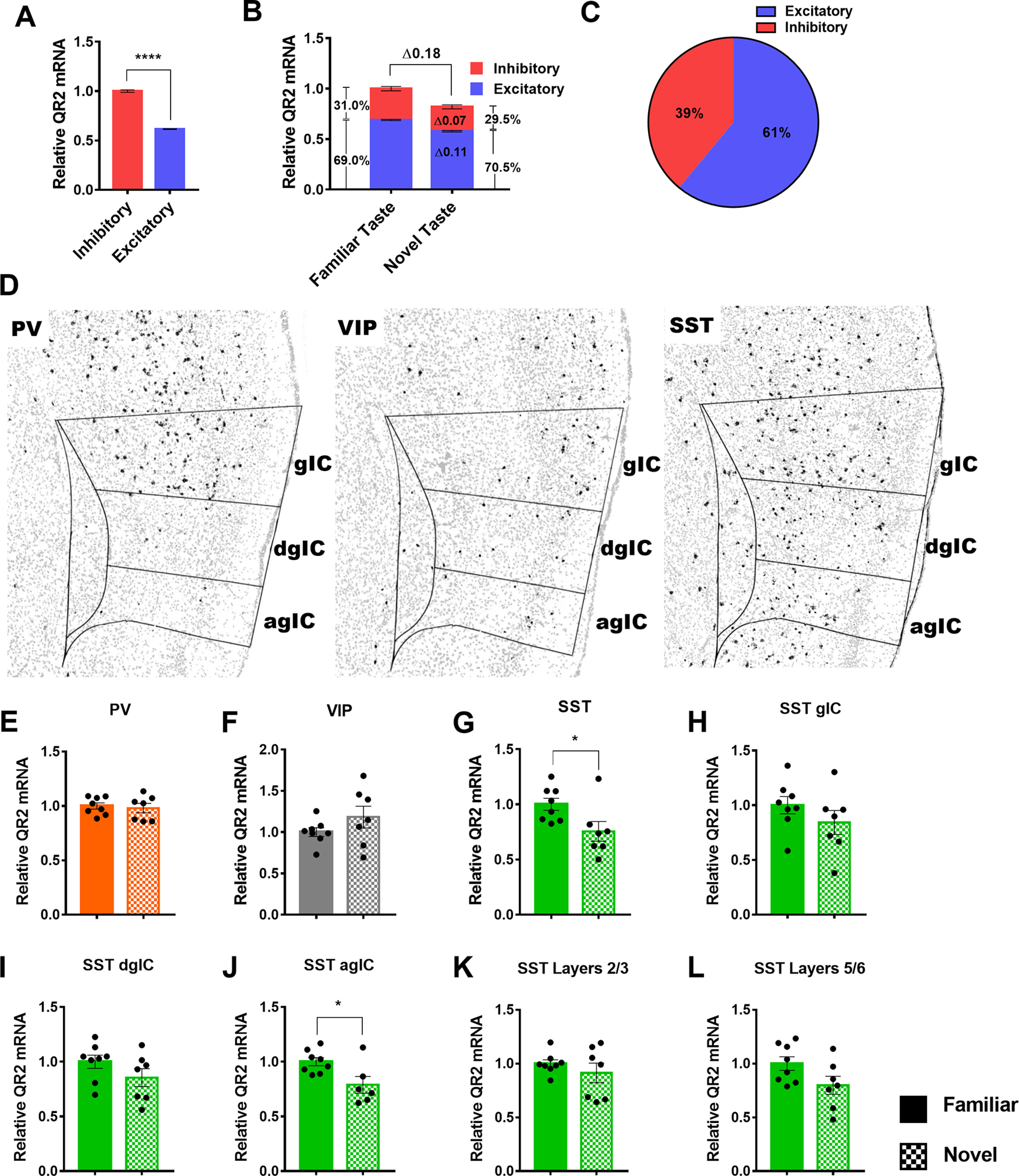
SST interneurons are the primary locus of QR2 expression reduction in the aIC following novel taste learning. A, Inhibitory neurons express roughly twice as much QR2 compared with excitatory neurons (inhibitory 1 ± 0.012 AU, cells n = 12,592 pooled from n = 14 mice; excitatory 0.614 ± 0.003, cells n = 45,749 pooled from n = 14 mice; Mann–Whitney test, p < 0.0001). B, Relative contribution of inhibitory and excitatory neurons to QR2 mRNA signal in both familiar and novel taste groups, as well as relative contribution to signal reduction following novel taste. C, Percentage of the total QR2 mRNA reduction measured in the aIC, by cell type. D, Representative distribution of PV, VIP, and SST interneurons in the aIC of mice, using RNAscope FISH. Outlines denote aIC and subregions (gIC, granular IC; dsIC, disgranular IC; agIC, agranular IC). E, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly altered in PV-expressing interneurons in the aIC following novel taste consumption (PV, familiar 1 ± 0.028 AU, n = 8; PV, novel 0.980 ± 0.043 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 0.3954 df = 13, p = 0.6989). F, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly altered in VIP-expressing interneurons in the aIC following novel taste consumption (VIP, familiar 1 ± 0.052 AU, n = 8; VIP, novel 1.182 ± 0.132 AU, n = 7 mice; Student’s t test, t = 1.342 df = 13, p = 0.2025). G, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in the aIC following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.054 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.754 ± 0.088 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 2.413 df = 13, p = 0.0313). H, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in the gIC following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.078 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.841 ± 0.109 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 1.198 df = 13, p = 0.2525). I, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in the dgIC following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.060 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.854 ± 0.082 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 1.456 df = 13, p = 0.1692). J, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are significantly reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in the agIC following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.036 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.788 ± 0.076 AU, n = 6; Student’s t test, t = 2.694 df = 12, p = 0.0195). K, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in layers 2/3 following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.035 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.912 ± 0.090 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 0.9477 df = 13, p = 0.3606). L, QR2 mRNA FISH-labeled expression levels are not significantly reduced in SST-expressing interneurons in layers 5/6 following novel taste consumption (SST, familiar 1 ± 0.062 AU, n = 8; SST, novel 0.797 ± 0.084 AU, n = 7; Student’s t test, t = 1.956 df = 13, p = 0.0722). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05.
